What Sets Cabinet Fans Apart from Other Cooling Solutions
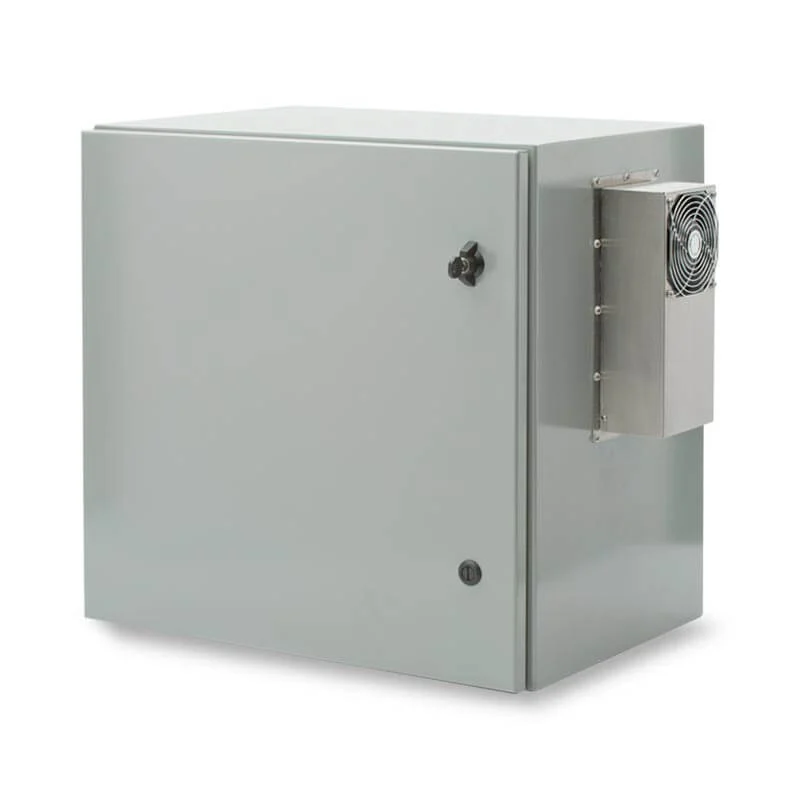

A Cabinet Fan offers a specialized approach to cooling enclosed electronics and AV cabinets. This solution directs airflow exactly where equipment needs it most, preventing heat buildup in small, sensitive spaces. Many users value the quiet operation, which keeps noise levels low in offices or home theaters. Targeted airflow and compact design make this fan ideal for protecting valuable electronics in confined environments.
Key Takeaways
Cabinet fans cool enclosed electronics by directing airflow precisely where heat builds up, protecting sensitive equipment in small spaces.
These fans operate quietly and efficiently, making them ideal for offices, home theaters, and labs where noise matters.
Advanced features like digital controls and brushless motors allow users to adjust airflow and monitor temperatures easily.
Compared to air conditioners and heat exchangers, cabinet fans offer simpler installation, lower costs, and minimal maintenance for mild environments.
Regular filter cleaning and checking fan performance help maintain cooling efficiency and extend the life of your electronics.
Cabinet Fan Basics

How They Work
A Cabinet Fan operates on the principle of forced convection. Motor-driven blades, called impellers, create a pressure difference that draws cooler air into the enclosure and pushes warmer air out. This continuous airflow removes heat from sensitive electronics and maintains optimal temperatures. The effectiveness of a Cabinet Fan depends on several factors:
Airflow rate, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), determines how much air the fan moves.
Static pressure capability shows how well the fan can push air through dense environments or filters.
Fan design, such as axial, centrifugal, or cross flow, matches specific cooling needs.
Proper airflow relies on controlled fan operation and filtration. Laminar airflow, where air moves in parallel layers, prevents turbulence and ensures even cooling. Advances in fan technology include smart controls and real-time monitoring, which help maintain consistent airflow and temperature. Experimental tests have shown that fans can reduce temperature fluctuations in enclosed spaces, confirming their role in protecting equipment.
Metric | Analogy | Measures | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
Airflow (CFM) | Volume of water flow | Volume of air moved | Open environments, low-resistance areas |
Static Pressure | Water jet pressure | Force exerted by the fan | Dense environments, heatsinks, radiators |
Common Uses
A Cabinet Fan serves many roles in protecting electronics and equipment. It is commonly used in:
Data cabinets and server racks to prevent overheating and hardware failure.
Audio-visual cabinets in home theaters or studios, where quiet operation is important.
Industrial control panels and electrical enclosures, where dust and heat can damage components.
Laboratory equipment cabinets, which require stable temperatures for sensitive instruments.
Empirical data shows that well-ventilated cabinets can reduce overheating risk by up to 30% compared to room-level cooling. Perforated doors and blanking panels further improve airflow and cooling efficiency. Fan speed control and temperature sensors help maintain safe operating conditions, while high-efficiency filters protect against dust and contaminants. These features make a Cabinet Fan a reliable choice for maintaining equipment performance and extending lifespan.
Features
Quiet Operation
Cabinet fans stand out for their quiet operation, which is essential in environments like offices, home theaters, and laboratories. Manufacturers design these fans with noise reduction as a priority. For example, the AIRPLATE T3 cabinet fan system achieves ultra-quiet performance, with noise levels measured at just 18 dBA. This low noise output results from a custom motor and dual ball bearings, which also extend the fan's lifespan.
Certification standards play a key role in verifying quiet operation. The UL-507 standard ensures safety compliance, while CE and RoHS certifications confirm environmental and safety standards. Testing organizations such as the Home Ventilating Institute (HVI) use procedures like HVI 915 for loudness and HVI 916 for airflow to certify fans. ANSI/AMCA Standard 300 also provides a method for sound testing.
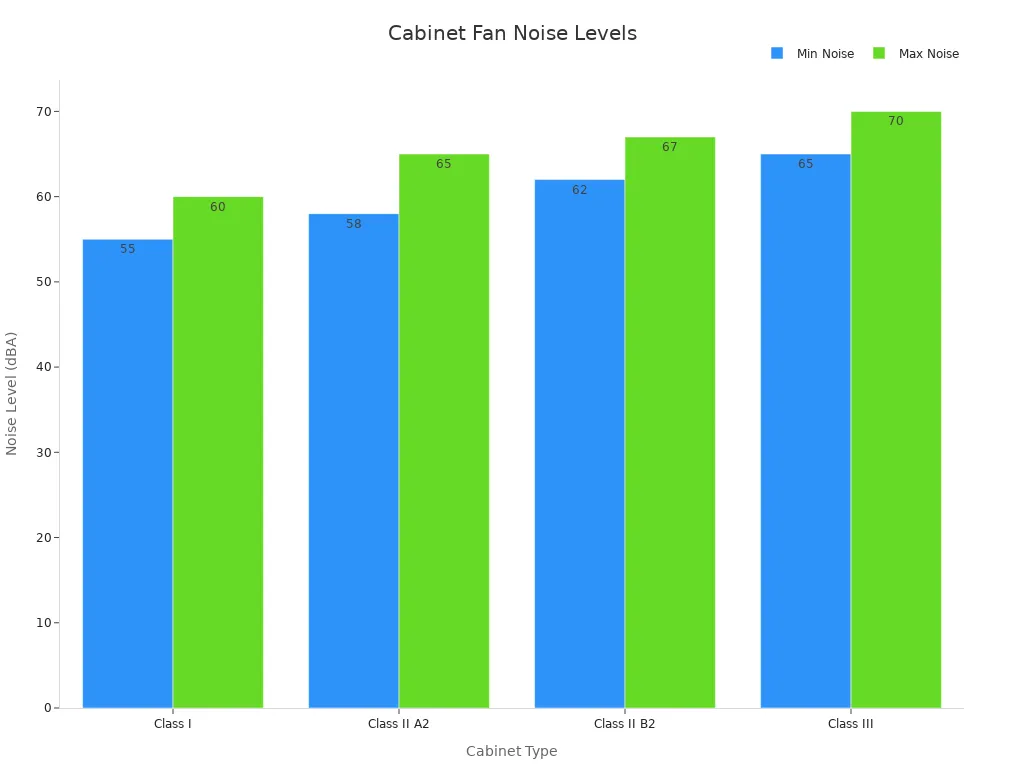
Noise levels vary by cabinet type and application. The following table shows typical noise ranges for different cabinet classes:
Cabinet Type | Typical Noise Level Range (dBA) | Measurement Conditions and Notes |
|---|---|---|
Class I | 55-60 | Measured at operator position under controlled conditions; simpler design results in lower noise levels. |
Class II A2 | 58-65 | Noise measured at 1 meter distance, seated operator height; balances protection and noise, common in labs. |
Class II B2 | 62-67 | Higher noise due to increased airflow and filtration; measurements follow NSF/ANSI 49 standard (max 67 dBA). |
Class III | 65-70 | Highest noise levels due to enclosed design and complex filtration; measurements standardized for comparability. |
Tip: When selecting a cabinet fan for noise-sensitive environments, always check for UL certification and review the product's decibel rating.
Airflow Control
Precise airflow control sets cabinet fans apart from many traditional cooling devices. These fans use advanced motor technology, such as brushless DC motors, to deliver consistent and adjustable airflow. Electronic controllers and variable speed options allow users to fine-tune performance based on equipment needs.
Testing standards require that cabinet fans maintain at least 70% of their airflow at a static pressure of 0.25 inches of water gauge compared to 0.1 inches. This ensures reliable performance even when filters or dense equipment restrict airflow. The Home Ventilating Institute (HVI) and ASHRAE standards guide these airflow tests.
Aspect | Energy-Efficient Cabinet Fans (BLDC) | Traditional Cooling Devices (AC Fans, Air Conditioners) |
|---|---|---|
Power Consumption | Up to 70% reduction compared to traditional AC fans | Higher power usage due to refrigerant cycles and AC motors |
Airflow Control | Precise management via electronic controllers and variable speed options | Less precise, often fixed speed or less adaptable airflow control |
Motor Technology | Brushless DC motors offering quieter operation and longer lifespan | Traditional AC motors, noisier and less efficient |
Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to reduced electricity use | Higher environmental footprint due to refrigerants and energy use |
Application Suitability | Ideal for smaller spaces, electronics cooling, automotive, energy-sensitive scenarios | Better for rapid cooling in large or high-heat environments |
Operational Costs | Lower due to energy savings and intelligent controls | Higher due to greater energy consumption and maintenance |
Technology Integration | Supports intelligent tech and variable speed for customized airflow | Limited integration, less flexible control |
Cabinet fans also offer options for intake or exhaust airflow direction, filter fans for dust protection, and NEMA-rated enclosures for harsh environments. These features help maintain optimal temperatures and protect sensitive electronics.
Digital Controls
Modern cabinet fans often include digital controls that enhance usability and precision. Many models feature LCD controllers with built-in thermostats, allowing users to monitor temperature and adjust fan speed automatically. This technology helps maintain stable conditions inside enclosures without manual intervention.
Digital controls support both AC and DC fan options, giving users flexibility based on power requirements. Some systems allow remote monitoring or integration with building management systems. These features make cabinet fans suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial control panels to home AV cabinets.
Note: Digital controllers not only improve energy efficiency but also extend equipment life by preventing overheating and reducing unnecessary fan operation.
Comparison

Cabinet Fan vs. Outdoor Cabinet Air Conditioner
A Cabinet Fan provides targeted airflow for enclosed electronics in mild or moderate climates. It uses less energy and offers a simpler installation process. Outdoor cabinet air conditioners deliver precise temperature and humidity control, making them ideal for hot, humid, or extreme environments. These systems protect sensitive equipment from moisture and heat, reducing the risk of packet loss and equipment failure. However, air conditioners require more complex installation and higher upfront costs, often ranging from $3,000 to $15,000 or more. They also consume more energy due to compressors and refrigerants.
Factor | Cabinet Fan | Outdoor Cabinet Air Conditioner |
|---|---|---|
Installation Ease | Simple, low cost | Complex, high cost |
Energy Efficiency | High, up to 80% savings | Lower, higher operational costs |
Maintenance | Minimal, easy | Frequent, more involved |
Environmental Suitability | Mild, clean environments | Harsh, humid, or extreme conditions |
Cooling Precision | Moderate | High, precise control |
Cabinet Fan vs. Outdoor Cabinet Heat Exchanger
Heat exchangers use the temperature difference between inside and outside air to remove heat. They work best in dry, dusty, or polluted environments because their closed-loop design keeps contaminants out. Their cooling capacity depends on ambient conditions, so they may not maintain a steady temperature if the outside air is too warm or too cold. Air conditioners can maintain a set temperature regardless of outside conditions, while a Cabinet Fan offers moderate cooling for less demanding applications. Heat exchangers require less maintenance and energy than air conditioners, making them suitable for remote or off-grid locations.
Air conditioners excel in hot, humid climates and high-density enclosures.
Heat exchangers suit dry, dusty, or polluted areas.
Cabinet fans work best in mild, clean environments with moderate heat loads.
Installation and Maintenance
Cabinet fans stand out for their easy installation and low maintenance needs. Users can often install them with basic tools and minimal downtime. Maintenance usually involves cleaning or replacing filters and checking for unusual noises. In contrast, air conditioners and heat exchangers need more frequent and detailed inspections. Typical maintenance schedules include monthly filter checks, quarterly equipment inspections, and annual system overhauls. Cabinet fans save time and reduce operational costs, making them a practical choice for many applications.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
Cabinet fans offer several practical benefits for cooling enclosed electronics and equipment. Many technical reviews highlight these advantages:
Simple installation process with fewer components than liquid cooling or compressor-based systems.
Lower upfront costs, making them accessible for small businesses and home users.
Minimal maintenance requirements, often limited to occasional filter cleaning.
No risk of leaks, unlike liquid cooling systems that use fluids.
Effective performance in low-to-moderate heat environments, especially when outside air is cooler than the equipment.
Reliable operation, as fans pull cool air through the enclosure and push out warm air, maintaining a steady temperature.
Users appreciate that air cooling systems, including cabinet fans, do not require specialized skills for setup or operation. This simplicity reduces downtime and ensures consistent protection for sensitive electronics.
A comparison of cooling solutions shows that air cooling systems provide a balance of performance and convenience:
Cooling Solution Type | Key Advantages |
|---|---|
Compressor-based ACs | High cooling power, compact designs |
Thermoelectric Coolers | Precise control, no refrigerants, compact |
Vortex Coolers | No moving parts, clean dry air, reliable |
Heat Exchangers (Air-to-Air) | Passive cooling, reliable, no moving parts |
Air Cooling (Fans) | Simple install, low cost, minimal maintenance |
Drawbacks
Despite their strengths, cabinet fans have some limitations compared to other cooling devices:
Limited cooling capacity in high-heat or humid environments.
Higher energy consumption than liquid cooling systems, especially in large installations.
Dependence on air-handling systems can increase overall energy use.
Less effective humidity control, sometimes requiring separate dehumidifiers.
Frequent filter cleaning may be necessary to maintain airflow and performance.
Consumer feedback and comparative tests indicate that while air-cooled cabinets are easy to maintain, they may not suit every application. For example, liquid cooling systems use less energy and provide better performance for high-density or mission-critical equipment. Compressor-based air conditioners offer precise temperature control but require more complex installation and maintenance.
When choosing a cooling solution, users should consider the specific heat load, environment, and maintenance resources available.
Selecting the right cooling solution depends on understanding equipment heat loads, environmental factors, and efficiency ratings. Industry reports show that cooling fans help maintain stable temperatures, extend equipment life, and improve reliability. They also support energy efficiency goals by reducing unnecessary power use. Users should calculate total heat output, consider ambient conditions, and review manufacturer data before choosing a cooling method. This approach ensures sensitive electronics remain protected and systems operate safely.
Consistent internal temperatures prevent overheating.
Energy-efficient fans support sustainability and lower costs.
Real-time monitoring improves operational efficiency.
Careful evaluation leads to informed decisions and optimal equipment performance.
FAQ
What makes a cabinet fan different from a regular fan?
A cabinet fan targets airflow inside enclosed spaces. It cools electronics directly and prevents heat buildup. Regular fans move air in open rooms. Cabinet fans often include filters, digital controls, and quiet operation for sensitive environments.
What environments benefit most from cabinet fans?
Cabinet fans work best in offices, home theaters, server rooms, and laboratories. These spaces need quiet, targeted cooling for electronics. They also suit industrial control panels and AV cabinets where heat buildup threatens equipment.
What features should users look for in a cabinet fan?
Key features include adjustable airflow, digital temperature controls, UL certification, and brushless motors. Some models offer filter fans for dust protection and NEMA-rated enclosures for harsh conditions.
Tip: Always check for energy efficiency and noise ratings before choosing a cabinet fan.
What maintenance does a cabinet fan require?
Users should clean or replace filters regularly. They should check for dust buildup and listen for unusual noises. Most cabinet fans need minimal maintenance compared to air conditioners or liquid cooling systems.
See Also
Industrial Benefits of ESTEL Cooling Solutions for Cabinets
Selecting The Optimal Cooling Approach For ESTEL Telecom Cabinets
Evaluating Various Cooling Techniques Used In Telecom Cabinets
The Importance Of Air Conditioning For Outdoor Communication Cabinets
Air Conditioning Solutions Tailored For Outdoor Telecom Cabinets
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA

