How Power Inverters Work for Home and Industry

A power inverter changes direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), letting you use standard appliances with battery or solar power. You rely on an inverter for backup power at home, in RVs, boats, telecom cabinets, and industrial sites. The demand for inverters keeps rising as more people adopt solar energy and smart technologies.
The power electronics market is set to reach $76.24 billion by 2032, boosted by electric vehicles, renewable energy, and smart grid projects worldwide.
Understanding how a power inverter works helps you choose the right model for your needs and use it safely and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
Power inverters change direct current (DC) from batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by most appliances.
Modern inverters produce smooth sine waves, improving safety and efficiency for sensitive devices.
Choosing the right inverter means matching its wattage and voltage to your devices and power sources, with extra capacity for safety.
Inverters help save money by using stored solar energy, support grid stability, and enable backup power during outages.
Proper installation, certified equipment, and regular maintenance keep your inverter system safe and reliable.
Power Inverter Basics
What Is a Power Inverter
A power inverter is a device that changes direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC), which most household and industrial appliances use. You often find a power inverter at the heart of backup power systems, solar energy setups, and even in telecom cabinets. When you use a power inverter, you can run your lights, computers, and other electronics with stored or renewable energy. This technology bridges the gap between modern appliances and alternative energy sources.
How It Works
You start with a DC power source, such as a battery or a solar panel. The inverter takes this DC electricity and uses electronic circuits to switch it rapidly, creating an AC waveform. This process allows you to power devices that require AC electricity, like refrigerators, televisions, and industrial equipment.
Tip: Many modern inverters use advanced electronics to produce a smooth sine wave, which closely matches the electricity from the grid. This ensures sensitive devices run safely and efficiently.
The evolution of inverter technology has been remarkable:
Early inverters performed basic DC-AC conversion.
Hybrid inverters now integrate battery management, improving system efficiency by about 10%.
AI and machine learning help manage energy flow, predict loads, and reduce losses, boosting energy yield by up to 20%.
Multi-MPPT inverters maximize energy harvesting, even when solar panels face different directions or shading, achieving conversion efficiencies over 98.7%.
Grid-tied inverters stabilize the grid and support renewable energy growth.
New designs focus on modularity, scalability, and remote monitoring, making maintenance easier and reducing costs.
Silicon carbide (SiC) technology has pushed inverter efficiency above 98%.
Several studies have tested inverter performance in real-world settings:
Researchers like Chen et al. (2013) and Luoma et al. (2012) used simulation tools to optimize inverter sizing and performance.
These studies show that the right inverter setup can lower energy costs, reduce emissions, and improve system reliability.
For example, Shezan et al. (2016) found that optimizing off-grid systems with inverters cut net present costs by nearly 30% and reduced CO2 emissions.
Why It Matters
A power inverter plays a key role in making alternative energy practical for your home or business. You gain the ability to use stored solar energy during outages or peak demand, which can lower your electricity bills and boost reliability. Inverters also help stabilize the grid and support the integration of renewable energy.
Here’s a quick look at how inverters impact energy reliability and cost savings:
Aspect | Impact of Power Inverters |
|---|---|
Inverter Efficiency | Converts DC to AC with up to 98.5% efficiency, maximizing usable energy. |
Functional Roles | Supports bidirectional power flow, voltage regulation, and seamless switching between grid and off-grid modes. |
Cost Savings | Lets you reduce electricity bills by up to 35% by storing solar energy and using backup power. |
Grid Reliability | Reduces outage duration and frequency, improving overall reliability. |
Economic Impact | Enables energy arbitrage and revenue generation through smart energy management. |
Rapid Response | Reacts in milliseconds to grid changes, helping prevent blackouts. |
Renewable Integration | Smooths power supply and provides backup during fluctuations. |
Job and Investment | Supports jobs and investments in the energy storage industry. |
You see the benefits of a power inverter in many places: homes, telecom cabinets, factories, and off-grid cabins. As technology advances, inverters become smarter and more efficient, helping you get the most out of your electricity—whether you rely on solar panels, batteries, or the grid.
Types and Applications
Sine Wave Inverters
You often choose between pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters create an AC output that closely matches the electricity from the grid. This type works best for sensitive electronics, medical devices, and appliances with motors. Modified sine wave inverters use a simpler waveform. These inverters cost less and work well for basic devices like lights or fans, but they may cause noise or reduced efficiency in some equipment.
Inverter generators combine a generator with an inverter circuit. You get stable, clean power for outdoor activities or backup needs. This makes them popular for RVs, boats, and portable power stations.
Off-Grid and Grid-Tied
You can use a power inverter in both off-grid and grid-tied systems. Off-grid inverters let you run appliances using batteries or solar panels when you have no access to the utility grid. Grid-tied inverters connect your solar panels to the public grid. These inverters allow you to send excess electricity back to the grid, often earning credits on your bill.
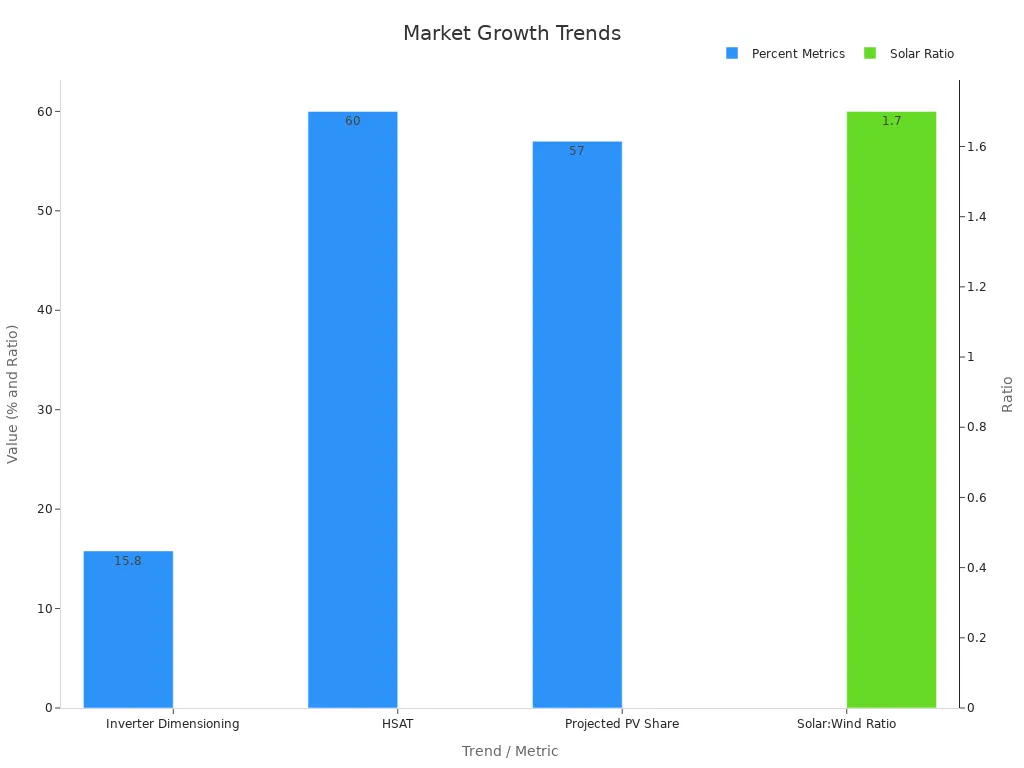
Recent market trends show strong growth for both off-grid and grid-tied systems. The table below highlights key factors driving this expansion:
Trend/Metric | Description | Impact on Market Growth |
|---|---|---|
Inverter Dimensioning (Undersizing) | Inverters are sized smaller than PV DC capacity because PV rarely generates full capacity; common DC/AC ratios are 1.5 to 1.7 in Europe. | Reduces investment cost by ~15.8%, making solar PV systems more cost-effective and driving adoption. |
Horizontal Single-Axis Tracking (HSAT) | PV modules rotate east to west, extending generation hours; holds 60% market share in new utility PV installations (2023–2024). | Increases solar generation efficiency and system attractiveness, supporting market expansion. |
Projected Solar PV Share | Solar PV projected to contribute 57% of electricity generation under self-sufficiency scenarios. | Highlights dominant role of solar PV and associated inverter systems in future energy markets. |
Telecom, Solar, and Off-Grid Uses
You see power inverters in many applications. In telecom cabinets, inverters ensure reliable AC power for communication equipment, even during outages. In solar PV systems, you use string inverters or microinverters for homes and small businesses. Central inverters handle large-scale solar parks and industrial sites, managing electricity from hundreds of panels with high efficiency.
You also find inverters in RVs, boats, and remote cabins. These systems let you enjoy modern comforts far from the grid. Hybrid inverters and power optimizers help you get the most from your solar panels, even if you face shading or complex layouts.
Technical reports show that string and microinverters dominate residential and small commercial solar installations. Central inverters serve industrial and utility-scale projects, where they deliver efficiency rates above 98%. This breakdown helps you choose the right inverter for your needs, whether you power a home, a telecom cabinet, or an industrial facility.
Using a Power Inverter
Choosing the Right Inverter
When you select a power inverter, you need to match it to your specific needs. Start by listing all the devices you want to run. Add up their wattage and include extra capacity for safety. For example, if your appliances total 2,400 watts, you should choose a 3,000-watt inverter. This gives you room for power surges and future expansion.
You also need to check the voltage of your battery system. Most homes and RVs use 12V, 24V, or 48V systems. Make sure your inverter matches this voltage. If you use solar panels or a generator, confirm that your inverter can handle these inputs.
Tip: Many buyers use real-time monitoring tools like the Cerbo GX controller or Victron Connect app. These tools help you track battery status, solar input, and AC output, making it easier to manage your system.
Key Features and Sizing
You want a power inverter with features that fit your application. Look for built-in transfer switches if you plan to use shore power or a generator. Some inverters offer Power Assist, which boosts AC power when your main source is not enough. Split-phase support is important for 120V/240V systems, especially in industrial or large residential setups.
Here is a quick checklist for sizing and features:
Calculate total appliance wattage and add a safety margin.
Match inverter wattage to your battery voltage (12V, 24V, or 48V).
Check input current limits and transfer switch capabilities.
Choose monitoring options for easy system management.
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Power Assist | Boosts AC power when needed |
Split-phase support | Runs both 120V and 240V appliances |
Real-time monitoring | Tracks system health and performance |
Safety and Certification
Safety comes first when using a power inverter. Always install your inverter according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use certified products that meet UL, CE, or other recognized safety standards. These certifications ensure your inverter has passed strict tests for electrical safety and performance.
Note: Proper installation and certified equipment protect your home, RV, or industrial site from electrical hazards.
By following these steps, you can enjoy reliable power and peace of mind when using a power inverter in any setting.
Installation and Troubleshooting
Setup Steps
You can install a power inverter in your home, RV, or telecom cabinet with a few clear steps. First, choose a location with good airflow and away from direct sunlight. Mount the inverter securely on a wall or shelf. Connect the DC input cables from your battery bank to the inverter terminals. Use cables with the correct gauge to handle the current safely. Attach the AC output wires to your main panel or dedicated outlets. Double-check all connections for tightness and correct polarity. Always follow the manufacturer's wiring diagram.
Tip: Turn off all power sources before you start wiring. This step keeps you safe during installation.
Integration with Solar and Batteries
You can boost your system by integrating the inverter with solar panels and batteries. Connect the solar charge controller between your panels and the battery bank. The controller manages charging and protects the batteries. The inverter draws DC power from the batteries and converts it to AC for your appliances. In telecom cabinets, you often use inverters to provide backup AC power for sensitive equipment. Many modern inverters support remote monitoring, which helps you track system performance and battery status.
Integration Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
Connect solar controller | Manages battery charging |
Link inverter to battery | Converts DC to AC for devices |
Enable monitoring | Tracks system health |
Common Issues
You may face some common inverter problems. Overloads happen when you connect too many devices. The inverter may shut down or beep. Low battery voltage can trigger alarms or reduce output. Surge capacity issues appear when starting motors or compressors. If your inverter does not turn on, check the fuses and battery voltage first. For telecom cabinets, ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating. Regularly inspect cables and terminals for corrosion or loose connections.
Note: If you see error codes, consult the manual for troubleshooting steps. Many issues resolve with a simple reset or by reducing the load.
You now understand how a power inverter converts DC to AC, making modern energy solutions possible for homes, telecom cabinets, and industry. When you select the right inverter, you ensure reliable power for your specific needs. Always follow safety guidelines during installation and check your system regularly. By applying these tips, you can improve your energy setup and keep your equipment running smoothly.
FAQ
What size inverter do you need for your home?
You should add up the wattage of all devices you want to run at the same time. Choose an inverter with at least 20% more capacity than your total wattage. This extra margin helps handle power surges.
Can you use a power inverter with solar panels?
Yes, you can connect a power inverter to solar panels through a battery bank. The inverter converts stored DC power from the batteries into AC power for your appliances.
Why do telecom cabinets use power inverters?
Telecom cabinets use power inverters to provide reliable AC power for communication equipment. Inverters ensure that systems keep running during outages or when only DC backup is available.
How do you maintain a power inverter?
Inspect cables and terminals regularly.
Keep the inverter clean and ensure good airflow.
Check for error codes and follow the manual for troubleshooting.
Test the system monthly to confirm proper operation.
See Also
Integrating Solar Inverters And Batteries With Telecom Cabinets
Solar Energy Storage Solutions Designed For Telecom Cabinets
Key Features To Understand About Telecom Power Supplies
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA
