Rectifier Module Selection Risks and Downtime Prevention for Telecom Cabinets

You face significant risks if you select an improper rectifier module for your telecom cabinets. Power interruptions from these modules can result in data loss and service outages, which directly harm network reliability and service availability. Industry reports show that even brief downtime disrupts operations, making redundancy essential for continuous power delivery. Proactive selection, regular maintenance, and strong operational practices help you minimize these costly interruptions.
Key Takeaways
Choose rectifier modules that match your telecom cabinet’s power, environmental, and communication needs to avoid damage and downtime.
Select high-efficiency, modular, and hot-swappable rectifiers to save energy, reduce heat, and enable easy maintenance without service interruption.
Follow strict installation and integration steps, including site preparation and wiring checks, to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Implement regular preventive maintenance and real-time monitoring to detect faults early and extend equipment life.
Use surge protection and redundant power setups to protect your system from failures and keep your network running continuously.
Rectifier Module Basics
Function in Telecom Cabinets
You rely on a rectifier module to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) power inside your telecom cabinet. This conversion is essential because telecom equipment operates on DC power. Leading telecom standards organizations define this function as the backbone of reliable network operation. The rectifier module ensures a steady energy supply, integrates with backup systems like batteries or generators, and protects sensitive devices with surge protection features. Modern modules achieve high efficiency—up to 97%—which supports uninterrupted service for advanced networks, including 5G.
Tip: Choosing the right rectifier module helps you maintain network stability and avoid costly downtime.
The most common types you will encounter are single-phase and three-phase bridge rectifiers. Single-phase units suit low-power applications, while three-phase models handle higher loads. Bridge rectifiers, using four diodes in a bridge configuration, deliver stable DC output and high efficiency. Many modern designs include power factor correction and soft-switching topologies to further boost reliability and energy savings.
Key Selection Criteria
When you select a rectifier module, you must evaluate several technical parameters to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
Efficiency: High efficiency reduces energy loss and operational costs. Advanced technologies like CoolGaN™ and SiC can exceed 95% efficiency.
Power Capacity: The module must meet the growing demands of telecom networks, especially with 5G deployments.
Power Quality: Power factor and total harmonic distortion affect equipment protection and network stability.
Dynamic Response: The ability to handle load fluctuations keeps your system stable.
Thermal Management: Effective cooling—air or liquid—extends module life and reliability.
Environmental Suitability: Modules must operate in harsh conditions, from -25°C to +55°C, and withstand dust and humidity.
Modularity and Scalability: Modular, hot-swappable designs allow easy expansion and maintenance without service interruption.
Redundancy and Hot-Swap Capability: Backup modules and quick replacement features minimize downtime.
Advanced Protection: Safeguards against voltage spikes, short circuits, and lightning protect your investment.
Remote Monitoring: Real-time tracking enables predictive maintenance and operational safety.
System Compatibility: Input/output voltage, size, and communication protocols must match your telecom system.
Durability and Reliability: High MTBF ratings and robust construction ensure long service life.
Cost Considerations: Balance initial investment with long-term savings and reliability.
Design Feature | Impact on Performance and Reliability |
|---|---|
Modular, hot-swappable units | Enable quick replacement and reduce downtime risks |
Wide voltage and current range | Support diverse telecom applications |
Environmental robustness | Ensure operation in extreme temperatures and harsh conditions |
Selecting the right rectifier module based on these criteria helps you build a resilient, efficient telecom infrastructure.
Rectifier Module Risks

Compatibility Issues
When you integrate a rectifier module into your telecom cabinet, you face several compatibility challenges. These issues can lead to equipment damage, system failures, and costly downtime if not addressed early. The most common compatibility problems include:
Voltage mismatches and improper power ratings that can damage sensitive equipment or cause system failures.
Failing to verify system specifications such as voltage, current, efficiency, and operating temperature, which can result in unstable operation.
Non-compliance with industry standards like NEBS Level 3, GR-3108, UL, CSA, or CE Marking, which may lead to regulatory issues or safety hazards.
Incompatible communication protocols (such as SNMP, HTTP, or Modbus) that prevent remote monitoring and control.
Efficiency losses from impedance mismatches and nonlinear components, which increase heat and complicate cooling.
Outdated designs that do not support growing power demands, leading to scalability and compatibility problems.
Complex installation processes that require specialized knowledge and tools, increasing deployment time and costs.
Environmental factors like temperature extremes, humidity, dust, power surges, and voltage instability that affect integration.
Challenges synchronizing with battery backup systems and communication equipment.
Inadequate ventilation and grounding, which can shorten equipment lifespan and reduce system stability.
Tip: Always match your rectifier module to your cabinet’s technical and environmental requirements to avoid costly integration issues.
Reliability Concerns
You depend on the rectifier module to deliver consistent power, but reliability can vary greatly depending on environmental and operational factors. Failure rates increase significantly when you move from controlled indoor environments to outdoor or transient conditions. For example, an LLC converter used in telecom settings shows a failure rate of about 0.082 failures per million hours in steady-state, controlled environments. This rate jumps to 0.3645 failures per million hours in transient, uncontrolled environments. The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) drops from roughly 12 million hours to just 2.7 million hours under harsher conditions.
Several factors contribute to these reliability concerns:
Thermal stress from fluctuating ambient and operating temperatures.
Electrical stress caused by voltage transients, surges, and sags.
Environmental stress from humidity and outdoor exposure.
Operational profiles that include frequent transient events.
High failure rates in semiconductors and capacitors within the rectifier module.
You must consider these risks when selecting and deploying rectifier modules, especially for outdoor or mission-critical telecom applications.
Operational Inefficiencies
Operational inefficiencies in your rectifier module can drive up energy consumption, increase maintenance costs, and reduce overall system reliability. The difference between an inefficient and an efficient rectifier module becomes clear when you compare their impact on your telecom cabinet’s performance:
Aspect | Inefficient Rectifier (92%) | Efficient Rectifier (96%) | Impact/Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
Annual Energy Consumption | ~95,652 kWh | ~91,667 kWh | Nearly 4,000 kWh saved annually per cabinet |
Annual Electricity Cost Savings | N/A | Over $600 saved | Direct reduction in electricity expenses |
Heat Generation | Higher heat output | Lower heat output | Reduced cooling requirements and operational costs |
Equipment Wear & Maintenance | Increased due to heat stress | Reduced due to better thermal management | Lower maintenance frequency and complexity |
Maintenance Features | Older, less modular | Modular, hot-swappable, smart monitoring | Enables early fault detection, remote management, and reduces downtime |
System Reliability | Lower due to inefficiencies | Higher due to advanced design | Extended equipment lifespan and improved uptime |
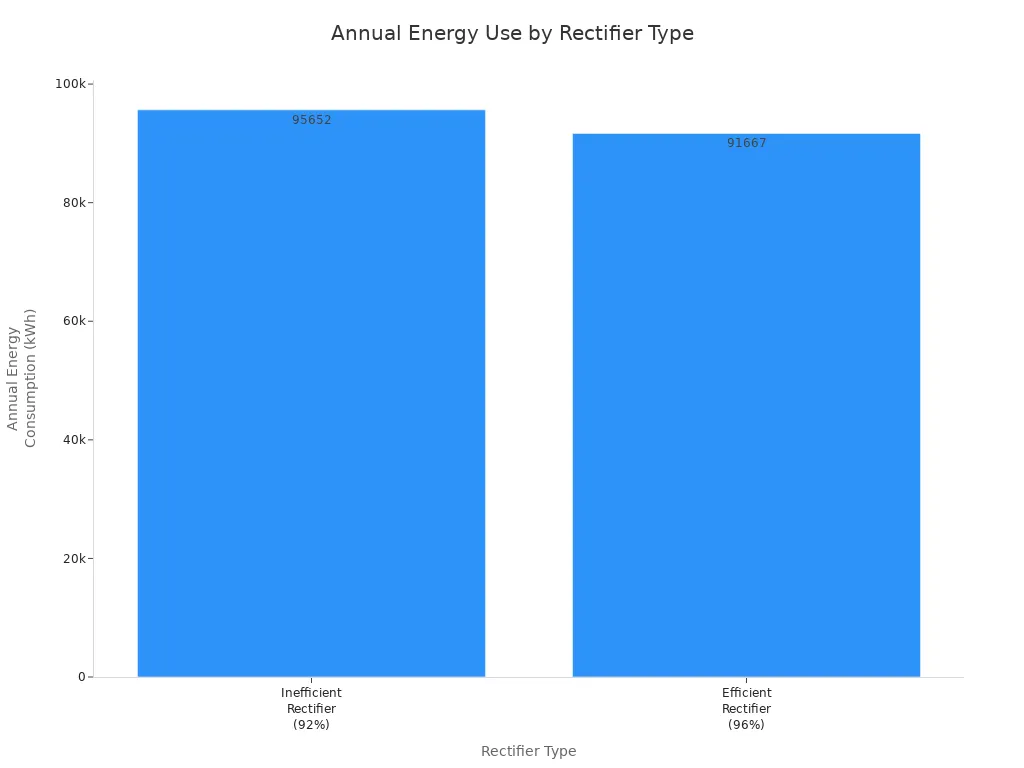
When you choose an efficient rectifier module, you not only save on electricity costs but also reduce heat generation. This leads to lower cooling requirements and less frequent maintenance. Advanced features like modularity and smart monitoring further improve uptime and system reliability. In contrast, inefficient modules increase operational costs and risk unplanned downtime.
Selection Criteria
Technical Specifications
You must evaluate technical specifications carefully when selecting a rectifier module for your telecom cabinet. Start by checking voltage and current compatibility to prevent equipment damage and ensure long-term reliability. High-efficiency ratings, reaching up to 96%, help you reduce power losses and lower operational costs. SCR-based designs deliver stable power and durability, especially in demanding telecom environments. Modular and scalable designs allow you to expand or maintain systems without disrupting service. Integration with existing power systems, including renewable sources, ensures seamless operation. IoT-enabled monitoring and support for protocols like SNMP provide real-time system health tracking. Compact, modular designs with effective thermal management simplify installation and boost reliability. You should also consider the availability of technical support, spare parts, and ease of troubleshooting to minimize downtime. Assess total cost of ownership over five to ten years, including energy consumption, maintenance, and replacement costs, to maximize your investment.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions play a critical role in the performance and lifespan of your rectifier module. Temperature variations can cause overheating, which shortens the life of electronic components. Efficient thermal management, using sensors, fans, and active cooling systems, maintains reliable operation. High humidity and dust increase the risk of short circuits and corrosion, which degrade system reliability. You can use dehumidifiers, protective coatings, and environmental monitoring to mitigate these risks. Adaptive control algorithms help maintain optimal conditions inside telecom cabinets. These protective measures ensure your rectifier module operates efficiently and lasts longer, even in harsh environments.
Vendor Assessment
Choosing the right vendor is essential for long-term system reliability. You should review the vendor’s track record in telecom power solutions. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards. Evaluate the vendor’s support services, including warranty terms, technical assistance, and spare parts availability. Reliable vendors offer transparent documentation and training resources. You benefit from strong after-sales support, which reduces downtime and ensures quick resolution of issues. Compare vendors using a table to simplify your decision:
Criteria | Vendor A | Vendor B | Vendor C |
|---|---|---|---|
Industry Certifications | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
Technical Support | 24/7 | Business hrs | Limited |
Spare Parts Availability | High | Medium | Low |
Warranty Terms | 5 years | 3 years | 1 year |
Tip: Select vendors with proven reliability, comprehensive support, and strong industry credentials.
Installation
Proper Procedures
You must follow strict procedures when installing power equipment in telecom cabinets. Start by preparing the installation site. Make sure the area is clean, dry, and free from dust or moisture. Good ventilation helps prevent overheating and extends the life of your equipment. Always review the manufacturer’s guidelines before you begin. These instructions provide details on mounting, wiring, and safety precautions.
Secure the equipment firmly to avoid vibrations. Loose mounting can damage internal components and cause system failures. Use only high-quality cables and connectors. Poor connections lead to power losses and increase the risk of short circuits. Double-check all wiring before powering up the system.
Note: Careful preparation and attention to detail during installation reduce the risk of early failures and costly downtime.
Integration Steps
You need to follow a clear sequence to integrate new power modules into your telecom cabinet system:
Prepare the site. Ensure it is clean, well-ventilated, and free from dust or moisture.
Follow the manufacturer’s mounting instructions closely.
Secure the module to prevent vibrations that could damage internal parts.
Use high-quality cables for all connections to the power system.
Verify every electrical connection to avoid power losses or short circuits.
Test the module under load conditions. Confirm it meets power requirements and operates efficiently.
Align voltage and current specifications with your telecom system for seamless operation.
Monitor performance metrics such as efficiency, reliability, and power density.
Address compatibility issues immediately to prevent disruptions.
Schedule regular maintenance to ensure reliable performance over time.
Tip: Careful integration and ongoing monitoring help you maintain system stability and prevent unexpected outages.
Maintenance

Preventive Actions
You extend the lifespan of your power equipment by following a structured preventive maintenance program. Start with regular visual inspections to spot physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections before they cause failures. Clean modules frequently using soft brushes or compressed air to remove dust and debris that can lead to overheating. Maintain ventilation and cooling systems by inspecting air filters, checking fan operation, and clearing blocked vents. Schedule firmware updates with care, verifying compatibility and monitoring the process to avoid malfunctions. Use predictive maintenance tools with sensors to monitor temperature and voltage in real time. Establish a routine maintenance schedule every three to six months, following manufacturer checklists and prioritizing tasks based on performance data. Train your maintenance team on technical and safety protocols, including personal protective equipment and lockout/tagout procedures.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Task | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Visual inspection | Monthly | Early fault detection |
Cleaning | Quarterly | Prevent overheating |
Ventilation check | Quarterly | Avoid thermal damage |
Firmware update | Semi-annual | Improve reliability |
Sensor monitoring | Continuous | Predict failures |
Team training | Annual | Ensure safe procedures |
Tip: Consistent preventive actions help you avoid costly downtime and extend equipment life.
Real-Time Monitoring
You improve system reliability by implementing real-time monitoring. This approach tracks key metrics such as voltage, temperature, power output, and battery health. Continuous tracking allows you to identify anomalies or faults before they escalate. Built-in safeguards like overload protection and thermal management detect issues proactively. Remote management capabilities let you address problems quickly, minimizing service interruptions. Integration with smart systems supports predictive maintenance, helping you forecast failures and reduce downtime. Secure remote control and multi-protocol support unify data from different devices, making monitoring more effective.
📊 Real-time alerts notify you of voltage drops or abnormal currents.
🛡️ Predictive analytics help you anticipate maintenance needs and optimize performance.
Cleaning and Inspection
You prevent failures by following best practices for cleaning and inspection. Clean modules every three to six months using a soft cloth or compressed air, avoiding liquid cleaners to prevent damage. Inspect all connections and components regularly, tightening loose connections and checking for rust or damage, especially on capacitors and diodes. Monitor voltage and current levels with sensors to detect early signs of failure. Maintain environmental controls by keeping the area free from dust, moisture, and overheating. Use cooling systems and dehumidifiers as needed. Schedule routine maintenance tasks, including monthly checks of connections and cleaning, quarterly firmware updates, and annual replacement or recalibration of parts. Use checklists during inspections to ensure all critical components are reviewed. Employ heat sensors to monitor temperature and prevent overheating caused by improper mounting or dust buildup. Address bad connections promptly by cleaning rust, tightening screws, and using quality cables.
Note: Adapt cleaning frequency based on environmental conditions such as dust or humidity to maintain optimal performance.
Protection and Redundancy
Surge Protection Devices
You protect your telecom cabinet from voltage spikes by using surge protection devices (SPDs). Voltage surges can damage sensitive power equipment and cause unexpected downtime. The most effective approach combines dedicated external surge protectors with modules that feature built-in surge protection. For example, some manufacturers design their modules with advanced internal safeguards that absorb and redirect sudden voltage spikes. When you use both external and internal protection, you create a strong defense against electrical disturbances. This strategy not only prevents immediate failures but also reduces long-term wear on your equipment. As a result, you extend the lifespan and reliability of your telecom infrastructure.
Tip: Always verify that your power equipment includes both external SPDs and internal surge protection features for maximum safety.
Redundant Configurations
Redundant power setups keep your telecom cabinet running even if a module fails. You achieve this by installing extra modules that automatically take over when one stops working. Hot-swappable designs let you replace or repair modules without shutting down the system. This flexibility is essential for telecom operations that require continuous power.
The table below shows how different redundancy types improve fault tolerance and reduce downtime:
Redundancy Type | Fault Tolerance | Maintenance Flexibility | Impact on Downtime Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
N+1 | Can handle one module failure without downtime | Allows moderate maintenance without shutdown | Ensures continuous power during a single failure, preventing downtime |
N+2 | Can handle two simultaneous module failures without downtime | Allows high maintenance flexibility without shutdown | Provides higher resilience, minimizing downtime risk during multiple failures or maintenance |
You benefit from these configurations by gaining higher system resilience and easier maintenance. Redundant setups ensure that your network stays online, even during repairs or unexpected failures.
Downtime Prevention
Risk Planning
You can prevent costly downtime by developing a comprehensive risk planning strategy. Start by identifying and assessing power resiliency challenges, such as single points of failure and aging infrastructure. Conduct risk assessments that consider natural disasters, cyber-attacks, equipment failures, and the overall health of your infrastructure. Analyze historical data on power anomalies and outages to find vulnerabilities. Engage with facility managers, IT teams, and safety leaders to gather a wide range of insights.
Follow these steps to build an effective risk plan:
Identify and assess all power resiliency challenges.
Conduct thorough risk assessments for various threats.
Analyze historical outage data to uncover weak points.
Consult with key stakeholders for diverse perspectives.
Develop and prioritize a detailed implementation plan.
Invest in infrastructure upgrades, including backup power systems.
Deploy advanced real-time monitoring and predictive analytics.
Establish robust maintenance programs with regular inspections.
Enhance emergency preparedness with response plans and drills.
Train staff continuously on power resiliency and emergency response.
Leverage innovative technologies like surge protection and smart grid integration.
Ensure compliance with safety and industry standards.
Monitor and improve strategies using KPIs and performance metrics.
Document all resiliency measures and incident responses.
Proactive risk planning helps you address vulnerabilities before they cause downtime.
Training and Readiness
You strengthen your downtime prevention efforts by focusing on staff training and operational readiness. Well-trained teams follow safety measures, such as lockout/tagout procedures, and conduct risk assessments to reduce electrical hazards. Modular rack mount designs allow you to isolate and replace faulty modules quickly, which keeps your system running during repairs.
Ongoing training ensures your team responds effectively to emergencies.
Hot-swappable modules enable maintenance without service interruptions.
Regular audits and real-time monitoring help you detect faults early.
Effective cable management reduces troubleshooting time and operational risks.
Routine inspections and drills improve response times and system reliability.
Continuous training and readiness keep your telecom cabinet resilient and minimize downtime.
You can reduce downtime and operational risks in telecom cabinets by combining modular design, advanced real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Case studies show that robust construction, high efficiency, and hot-swap capability deliver measurable improvements in reliability and energy savings. Continuous improvement in operational practices—such as regular inspections, tool-less maintenance, and proactive upgrades—ensures your power systems remain resilient and ready for future demands.
Stay vigilant and invest in ongoing training to keep your telecom infrastructure strong and dependable.
FAQ
What happens if you install an incompatible rectifier module?
You risk damaging your telecom equipment and causing unexpected downtime. Always check voltage, current, and communication protocol compatibility before installation.
How often should you perform preventive maintenance on rectifier modules?
You should inspect and clean your rectifier modules every three to six months. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and adjust the schedule based on your environment.
Why is redundancy important in telecom cabinet power systems?
Redundancy ensures your network stays online if a module fails. You can replace faulty modules without shutting down the system, which keeps your services running.
Can you monitor rectifier modules remotely?
Yes, you can use remote monitoring systems. These tools track voltage, temperature, and performance in real time. You receive alerts for faults, which helps you prevent downtime.
See Also
Steps To Guarantee Consistent Power For Telecom Cabinets
Solar Inverter And Battery Setup Connected To Grid For Telecom
Guide To Choosing And Mounting Telecom Cabinets On Poles Safely
Reasons Lithium Batteries Are Superior For Telecom Cabinet Power
Solar Energy Storage Solutions Designed For Telecom Cabinet Power
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA

