Understanding Rectifier Module Telecom Systems for Critical Power Needs
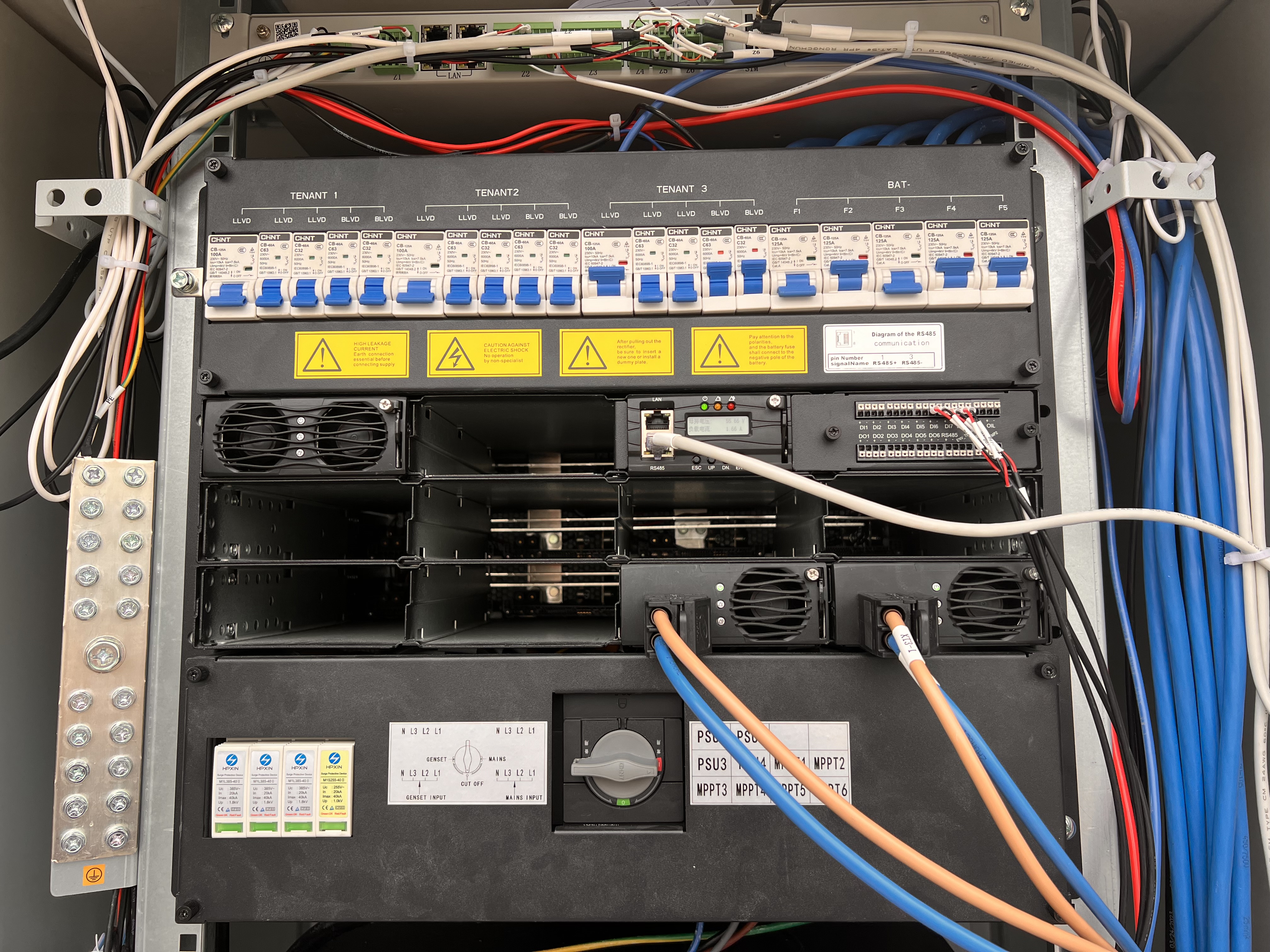
A sudden telecom outage can disrupt communication, threaten business operations, and impact safety. Rectifier module telecom systems play a vital role in maintaining reliable power for telecom infrastructure, ensuring continuous connectivity even when the grid fails. These systems convert AC to DC and support backup batteries, making them essential for critical infrastructure. Their reliability stands out in the industry, with mean times between failure reaching up to 200,000 hours and DC power system unavailability as low as 9×10^-10 with extended battery backup.
Metric / Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
Rectifier system configuration | 4000A system built from 21 or more 200A rectifier modules |
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) of rectifiers | Between 100,000 and 200,000 hours |
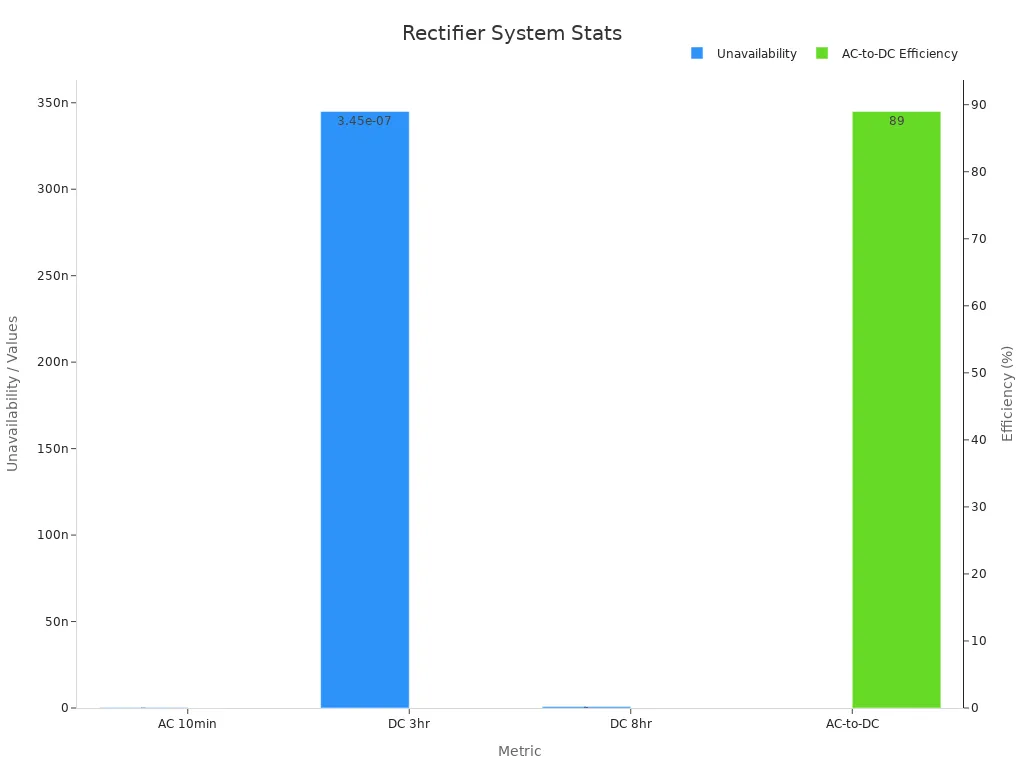
Unavailability of DC power system (8-hr battery backup) | Approximately 9×10^-10 |
Unavailability of AC UPS system (10-min battery backup) | Approximately 3.5×10^-10 |
Power load range for critical telecom systems | 7000A to 160,000A at -48VDC |
AC-to-DC efficiency of rectifiers | Average 89% |
Reliable rectifier module telecom systems support the backbone of modern telecom infrastructure, minimizing downtime and protecting essential infrastructure from power disruptions.
Key Takeaways
Rectifier module telecom systems convert AC power to stable DC power, ensuring continuous operation of telecom equipment even during power outages.
High efficiency in rectifiers reduces energy loss and operational costs while supporting environmental sustainability.
Modular design allows easy expansion and quick replacement of parts, minimizing downtime and adapting to growing network demands.
Remote monitoring and advanced protection features help detect issues early, improve safety, and maintain reliable power supply.
These systems are built to work reliably in harsh environments, supporting critical telecom infrastructure worldwide.
Rectifier Module Telecom Basics
What Is a Rectifier Module?
A rectifier module telecom system serves as a specialized ac to dc converter designed for the demanding requirements of telecom networks. The rectifier transforms alternating current (AC) from the utility grid into direct current (DC), which is essential for powering sensitive telecom equipment. Inside each rectifier, semiconductor diodes or silicon-controlled rectifiers arrange in specific circuits—such as half-wave, full-wave, or bridge configurations—to achieve this conversion.
The table below summarizes the main types of rectifiers and their applications in telecom:
Rectifier Type | Principle & Operation | Telecom Application & Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Half-Wave Rectifier | Converts one half of AC waveform to DC; low efficiency | Rare in high-performance telecom systems |
Full-Wave Rectifier | Uses both halves of AC waveform for smoother DC output | Common for stable, reliable telecom power |
Bridge Rectifier | Four diodes in bridge; efficient AC to DC conversion without center-tap | Widely used for high efficiency and compact size |
Three-Phase Rectifier | Designed for three-phase AC; stable DC with reduced ripple | Ideal for high-power telecom applications |
Modern rectifier modules often include heatsinks for thermal management and electronic filters to smooth the DC output. Voltage regulators ensure a steady voltage, which is critical for telecommunications rectifier systems. The modular design allows for scalability, enabling telecom operators to add or replace modules as network demands grow.
Role in Telecom Systems
Rectifier module telecom systems play a central role in maintaining uninterrupted operation of telecom infrastructure. As the primary ac to dc converter, the telecom rectifier supplies stable DC power to base stations, routers, and servers. This function becomes vital during grid outages, as the rectifier continues to charge backup batteries and deliver power to critical equipment.
Key functions of telecom rectifier modules include:
Converting grid AC to reliable DC for telecom devices.
Supporting battery backup systems to prevent service interruptions.
Enabling remote monitoring and advanced fault management for safety.
Allowing modular expansion to meet growing network needs.
The modular approach in rectifier module telecom systems ensures that telecom providers can scale their infrastructure efficiently. For example, the ESTEL system demonstrates how modular rectifiers achieve high efficiency and reliability, supporting both scalability and redundancy.
Telecommunications rectifier modules use advanced control circuits to maintain output stability. These circuits sample the output and adjust inverter frequency or pulse width, ensuring consistent performance even as load conditions change. The combination of robust design and intelligent control makes the telecom rectifier a cornerstone of modern telecom networks.
Power Reliability in Telecom

Impact of Power Loss
Power loss poses a significant threat to telecom infrastructure. When rectifier systems fail or grid interruptions occur, telecom networks experience immediate disruptions. These outages can halt data transmission, disconnect users, and damage sensitive equipment. The consequences extend beyond technical setbacks, often resulting in financial losses and diminished customer trust. Reliable rectifier modules and uninterrupted power supply solutions form the backbone of stable power delivery, ensuring uninterrupted communication services.
The following table outlines how different aspects of power management affect telecom network performance:
Aspect | Description | Impact on Telecom Network Performance |
|---|---|---|
Power Outages | Interruptions in electrical supply to telecom equipment | Cause service disruptions, financial losses, and customer dissatisfaction |
Power Control Systems | Manage and distribute power, including backup power | Ensure continuous operation, minimize downtime, and maintain network reliability |
Uninterruptible Power Supplies | Provide immediate backup power during grid failures | Prevent data loss and service interruptions by delivering clean, continuous power |
Battery Energy Storage Systems | Store energy to supply power during outages or peak demand | Support network uptime and load balancing, extend equipment life |
Power Management Challenges | Heat generation, scalability, remote/off-grid power supply | Improper management leads to equipment failure and reduced network performance |
Case Studies (5G, Infrastructure) | Advanced power control in high-density and remote networks | Demonstrate improved reliability and energy efficiency |
Reliable rectifier systems and advanced power management protect telecom infrastructure from the risks of power loss, supporting continuous operation and customer satisfaction.
Modern Network Demands
Modern telecom infrastructure faces unprecedented demands. The rapid expansion of 5G and increased data traffic require rectifier systems that deliver high efficiency and adaptability. Recent technical reports show that telecom operators now prioritize energy optimization and sustainability. Many networks integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into hybrid power systems to reduce costs and environmental impact. Smart monitoring and IoT-based control technologies enable real-time management, improving operational efficiency and reducing energy waste.
The North American market leads in adopting hybrid systems that combine renewables with traditional rectifier solutions, ensuring stable power for expanding infrastructure. Market research highlights that the surge in mobile tower construction and broadband adoption drives the need for reliable, energy-efficient rectifier modules. Telecom infrastructure in regions like the Middle East and Africa also shifts toward advanced energy storage and renewable integration, meeting the challenges of scaling and rising energy costs.
Rectifier modules must support stable power delivery, scalability, and remote management to keep pace with evolving telecom infrastructure. These innovations ensure that telecom networks maintain uninterrupted power supply and deliver uninterrupted communication services, even as digital demands grow.
Rectifier Module Telecom Features
High Efficiency
Modern telecom rectifier systems must deliver high efficiency to meet the demands of today’s telecom infrastructure. High efficiency reduces energy loss during AC to DC conversion, directly lowering operational costs and minimizing heat generation. The ESTEL 10U 36KW 48VDC Rectifier System achieves efficiency ratings above 96%, setting a benchmark for the industry. This level of performance ensures that telecom operators can support critical infrastructure with minimal waste and maximum reliability.
ESTEL rectifier modules consistently reach efficiency levels above 95%.
These systems convert AC to DC with minimal energy loss, supporting sustainable telecom operations.
Technical documentation for leading models, such as the VERTIV™ eSure™ R48-2000e3, confirms efficiency ratings exceeding 96%.
Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
Model | VERTIV™ eSure™ R48-2000e3 |
Output Power | 2000 W |
Efficiency | 96.2% |
Input Voltage | 85 to 300 VAC |
Output Voltage | -42 to -58 VDC |
Max Current | 42 A |
Power Factor | >0.99 |
High efficiency in telecom rectifier modules not only reduces energy bills but also supports environmental goals by lowering the carbon footprint of telecom infrastructure.
Modularity and Scalability
Telecom networks require flexible solutions that can grow with increasing demand. Modularity in rectifier design allows operators to add or replace modules as needed, ensuring seamless scalability. The ESTEL system exemplifies this approach, supporting up to twelve hot-swappable modules in a compact rack-mount design. This modularity enables telecom infrastructure to expand without major overhauls or service interruptions.
Modular rectifier systems simplify installation and maintenance. Operators can increase capacity by adding modules or replace faulty units without shutting down the system. In large-scale deployments, such as those in the Asia-Pacific region, over half of network expansions use high-efficiency, modular rectifiers to meet rising power needs. ESTEL rectifiers can scale up to 100 modules, delivering up to 300 kW, which allows customization for diverse telecom sites.
Modularity and scalability ensure that telecom infrastructure remains future-proof, supporting both current and emerging network requirements.
Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring and control have become essential features in advanced telecom rectifier systems. These capabilities allow operators to oversee system performance, diagnose issues, and adjust parameters from any location. The ESTEL 10U system integrates remote monitoring and control through Ethernet, SNMP, ModBus, and RS485 protocols, providing real-time access to critical data.
Remote monitoring uses wireless, cellular, satellite, and cable technologies for continuous data acquisition.
Operators receive automatic alerts for deviations, failures, or unauthorized access.
Smart sensors and cloud platforms enable predictive maintenance, reducing manual inspections and operational costs.
Real-time measurements and anomaly detection ensure high availability and operational safety.
Remote monitoring and control shift maintenance strategies from reactive to predictive, minimizing failures and optimizing resource allocation across telecom infrastructure.
Redundancy and Hot-Swap
High availability is a non-negotiable requirement for telecom infrastructure. Redundancy and hot-swap capabilities in telecom rectifier systems ensure continuous operation, even during maintenance or unexpected failures. The ESTEL system features hot-swappable modules, allowing technicians to replace faulty units in under a minute without shutting down the system.
Redundancy Configuration | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
1+1 Redundancy | One primary and one backup; backup takes over instantly if primary fails. | Small server setups |
N+1 Redundancy | Multiple units with one extra backup; uninterrupted power if one fails. | Data centers |
N+N Redundancy | Two independent systems in parallel; either can handle full load. | Financial institutions |
Hot-Swappable Systems | Modules replaced without system shutdown. | Telecom and cloud providers |
Redundant power supplies and hot-swap features minimize downtime, enhance reliability, and support uninterrupted service delivery. These features are critical for telecom rectifier systems deployed in mission-critical environments.
Advanced Protection
Advanced protection features safeguard telecom rectifier systems and the broader telecom infrastructure from electrical faults, surges, and environmental hazards. The ESTEL 10U system incorporates comprehensive protection mechanisms, including load power-off, battery low-voltage protection, secondary power-off, and lightning protection on both AC and DC sides.
Protection Aspect | Relevant Standards | Demonstrated Protection Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
Transient-Voltage Protection | EN61000-4-5, EN41003 | Resilience to voltage spikes |
Electromagnetic Compatibility | EN55022 | EMI/RFI limits and compliance testing |
Safety Standards | EN60950, UL950 | Isolation voltage and distance requirements |
Real-time monitoring tracks voltage, current, and temperature, enabling proactive detection and resolution of potential issues. Redundant configurations, such as N+1, ensure continuous power supply even if one module fails. Compliance with international standards further enhances the safety and reliability of telecom rectifier systems.
Advanced protection features reduce the risk of equipment damage, data loss, and service interruptions, ensuring the integrity of telecom infrastructure.
Telecom Rectifier Applications

Cell Towers
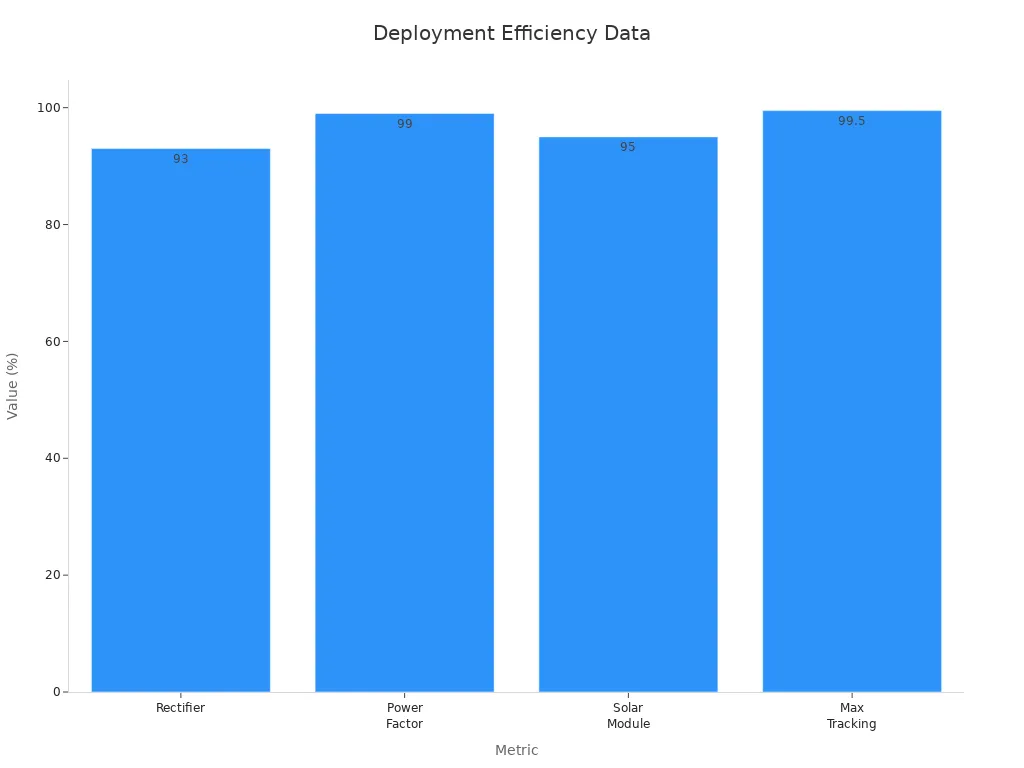
Cell towers form the backbone of modern telecom infrastructure. Operators rely on class 4 telecom rectifiers to deliver stable power to both macro and micro tower sites. These rectifiers support continuous operation, even during grid failures or maintenance. The ESTEL system, with its modular and hot-swappable design, allows technicians to replace modules in under a minute, minimizing downtime. Real-world deployments show that telecom rectifier modules achieve over 93% efficiency and a power factor up to 0.99. These features help reduce energy loss and operational costs while supporting renewable integration.
Feature | Practical Data / Metric |
|---|---|
Rectifier Efficiency | Over 93% efficiency in deployed telecom systems |
Power Factor Compensation | Up to 0.99, minimizing energy loss |
Solar Module Efficiency | Over 95%, supporting renewable integration |
Maximum Power Point Tracking | Accuracy over 99.5%, optimizing solar energy |
Modular & Hot-swappable | Modules replaceable in under one minute |
Battery Management | Automatic voltage regulation, online battery tests, fault protection |
Monitoring & Control | Real-time insights, 90 days historical data, 200 alarm records |
5G Infrastructure
5G infrastructure demands higher power capacity and reliability. Class 4 telecom rectifiers play a critical role in supporting dense network deployments and advanced features. Modern systems, such as the ESTEL rectifier, deliver over 91% AC to DC conversion efficiency and nearly double the power capacity of previous generations. These rectifiers include advanced protection mechanisms, modular scalability, and immediate shutdown features for technician safety. Operators benefit from energy-saving modes and intelligent monitoring, which align with sustainability goals and reduce operational costs.
Performance Aspect | Measurement / Feature | Impact on 5G Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | Over 91% efficiency in AC to DC conversion | Reduces energy loss and operational costs |
Power Capacity | Nearly double power compared to previous generations | Supports increased power demands of 5G networks |
Protection Mechanisms | Advanced safeguards against voltage fluctuations, short circuits | Ensures uninterrupted power delivery and system reliability |
Environmental Operating Range | -25°C to +55°C | Reliable operation in harsh and remote environments |
Scalability | Modular, hot-swappable design | Enables easy expansion and minimal downtime during maintenance |
Harsh Environments
Telecom infrastructure often operates in challenging conditions. Class 4 telecom rectifiers, such as those from ESTEL, are engineered for durability in extreme temperatures, humidity, and dust. These systems use corrosion-resistant coatings and advanced cooling to maintain performance. High efficiency above 95% ensures stable power output under varying loads. Maintenance-friendly features, including tool-less access and self-diagnostics, reduce operational interruptions. Rigorous testing simulates voltage fluctuations and temperature extremes, confirming long-term reliability.
Testing covers maximum average rectified current, reverse working voltage, and breakdown voltage.
Compliance with Energy Star, ISO 14001, CE, and UL standards ensures eco-friendly and sustainable operation.
Advanced semiconductor technologies and AI-driven optimization enhance reliability and reduce downtime.
Modular and compact designs support scalability and reduce material waste.
Certifications and compliance validate the reliability of class 4 telecom rectifiers, making them essential for critical telecom infrastructure in diverse environments.
Choosing the Right Rectifier

Key Selection Factors
Selecting the right rectifier for telecom applications requires careful evaluation of technical and operational needs. Engineers often compare key factors using expert analyses and practical benchmarks. The following table summarizes important metrics and their impact on performance:
Key Factor / Metric | Description / Comparison |
|---|---|
Power Factor | Advanced rectifiers like PWM achieve near unity power factor, improving power quality. |
Total Harmonic Distortion | Modern rectifiers reduce harmonic distortion, essential for telecom reliability. |
Efficiency | High-efficiency rectifiers minimize energy loss, supporting continuous operation. |
Dynamic Response | Advanced rectifiers handle load fluctuations effectively. |
Scalability | Modular designs allow expansion as demand grows. |
Durability | Robust construction ensures long-term reliability. |
Future-Proofing | Compact, modular designs support integration with renewables. |
Control Features | Advanced systems enable predictive maintenance and improved uptime. |
Engineers should review load requirements, including maximum current and voltage, to ensure the rectifier meets telecom system demands. Power quality remains critical, so rectifiers with low total harmonic distortion and strong dynamic response protect sensitive equipment. Modular designs offer scalability, allowing easy capacity expansion. Durability and reliability matter in harsh environments, so robust construction and proven performance are essential. Future-proofing through advanced control features and renewable integration supports evolving telecom infrastructure.
Cost and Efficiency
Cost and efficiency play a central role in rectifier selection. Operators must balance initial investment with long-term savings and operational reliability. The following table highlights decision-making insights for key selection factors:
Key Selection Factor | Description | Decision-Making Insight |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency Benchmarks | Use of advanced components to reduce losses and improve efficiency. | Select rectifiers with high efficiency to save energy costs. |
Cooling Methods | Air cooling suits low-medium power; liquid cooling fits high power needs. | Match cooling to environment for reliability and lifespan. |
Environmental Suitability | Consider temperature range and protective enclosures for harsh sites. | Align specifications with site conditions. |
System Connectivity | Real-time monitoring and modular design ease integration and maintenance. | Choose advanced connectivity for future expansion. |
Cost Considerations | Balance initial price, energy efficiency, and maintenance costs. | Invest in reliable rectifiers to lower total ownership cost. |
Maintenance & Longevity | Regular inspection and timely replacement extend lifespan. | Implement maintenance plans for consistent performance. |
Operators should always match rectifier specifications to the intended application. Reviewing technical datasheets and performance benchmarks ensures compatibility and efficiency. Application-specific recommendations help optimize rectifier selection for telecom, industrial, or renewable energy systems.
Tip: Always consult technical specifications and performance data before making a final decision. This approach ensures the rectifier will meet both current and future telecom requirements.
Rectifier module systems deliver reliable, efficient, and safe power for telecom infrastructure. Their modular design supports easy upgrades and future expansion. Advanced features, such as redundancy and remote monitoring, enhance equipment longevity and operational safety. The table below highlights key benefits and projections for advanced rectifier solutions:
Aspect | Summary of Benefits |
|---|---|
Energy Savings | Up to 100x lower energy use with new technologies |
Longevity | Protection features extend equipment life |
Scalability | Modular design supports network growth |
Market Growth | Projected 8.3% CAGR through 2033 |
As telecom networks evolve, advanced rectifier systems will address new power challenges and support sustainable, resilient connectivity.
FAQ
What is the main function of a rectifier module in telecom systems?
A rectifier module converts alternating current into direct current. This process ensures stable power delivery to telecom equipment. Operators rely on rectifier modules to maintain uninterrupted service during grid failures or fluctuations.
How does modularity benefit telecom rectifier systems?
Modular rectifier systems allow operators to add or replace modules as network demands change. This design supports easy expansion and maintenance. Technicians can quickly swap modules, reducing downtime and improving overall power reliability.
Why is high efficiency important in telecom rectifiers?
High efficiency reduces energy loss during conversion. Efficient rectifiers lower operational costs and minimize heat generation. This helps telecom providers maintain reliable power while supporting sustainability goals.
What protection features do advanced rectifier systems offer?
Advanced rectifier systems include protection against voltage surges, short circuits, and lightning. These features safeguard both the rectifier and connected telecom equipment, ensuring continuous power supply and reducing the risk of equipment damage.
Can rectifier modules operate in harsh environments?
Yes, many rectifier modules feature robust construction and advanced cooling. These systems perform reliably in extreme temperatures, humidity, and dust. Telecom operators can deploy them in remote or challenging locations without sacrificing power stability.
See Also
Methods To Calculate Power Systems And Batteries For Telecom
Introductory Guide To Telecom Power Supply System Basics
Steps To Guarantee Stable Power Supply In Telecom Cabinets
Key Information About Features Of Telecom Power Supplies
Solar Inverter And Battery Systems Connected To Grid For Telecom
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA
