How ESTEL Telecom Equipment Monitoring Software Detects and Prevents Network Issues

ESTEL telecom equipment monitoring software uses advanced monitoring tools to detect network problems as soon as they appear. The software tracks network devices, collects data, and analyzes patterns to identify threats or failures. Real-time monitoring helps operators see network health instantly. The software uses automated alerts to notify teams when network data shows signs of trouble. By acting quickly, telecom equipment monitoring software can prevent outages and keep the network stable. This approach protects vital network infrastructure and improves service reliability.
Key Takeaways
ESTEL monitoring software tracks network devices in real time to detect problems early and prevent outages.
The software collects and analyzes key metrics like latency, packet loss, and bandwidth to keep networks healthy.
Instant alerts notify teams about issues so they can act quickly and reduce downtime.
Automated responses help fix problems fast by rerouting traffic or restarting devices without manual work.
Using ESTEL’s software improves network reliability, saves costs, and ensures service quality for telecom operators.
Telecom Equipment Monitoring Software
What It Does
Telecom equipment monitoring software serves as the backbone of modern network management. This software monitors devices, applications, and infrastructure across both physical and cloud environments. It collects data from routers, switches, firewalls, and servers, tracking metrics like uptime, CPU usage, bandwidth, and latency. Network monitoring software uses protocols such as SNMP to gather telemetry data, ensuring that every device and application remains healthy and available.
Real-time monitoring of network traffic and performance
Early detection of issues to prevent downtime
Continuous data collection on usage and equipment health
Environmental monitoring for temperature and physical threats
Detailed reporting and analytics for troubleshooting and planning
Scalability for expanding networks and cloud integration
Support for multiple protocols, including legacy systems
User-friendly interfaces and customizable APIs for automation
Network monitoring software validates these functions through industry-standard testing tools. Tools like Wireshark and Spirent TestCenter simulate real-world conditions, verifying performance and security. This ensures that telecom equipment monitoring software meets the demands of complex, hybrid networks.
Why It Matters
Network monitoring plays a critical role in telecom operations. Operators rely on network monitoring software to maintain end-to-end visibility across all network layers, from physical devices to cloud-based applications. This visibility allows engineers to monitor device health, application performance, and network traffic in real time.
Effective network monitoring software provides unified monitoring across on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments. It consolidates network data, infrastructure metrics, and application analytics, enabling rapid identification and resolution of issues.
Network monitoring tools track device availability, performance metrics, and security compliance. They monitor latency, storage, VoIP quality, and hardware health, addressing challenges like capacity planning and security requirements. Cloud network monitoring extends these capabilities to virtualized and containerized environments, supporting primary use cases for network monitoring such as datacenter and cloud network monitoring.
Network monitoring software needs to provide comprehensive visibility and actionable insights. This enables telecom operators to optimize network management, prevent outages, and ensure reliable service delivery. When considering a network monitoring software purchase, organizations should prioritize solutions that offer end-to-end visibility, robust monitoring tools, and seamless integration with existing systems.
Network Monitoring Mechanisms

Real-Time Data Collection
Network monitoring software relies on real-time data collection to maintain the health and stability of telecom networks. This process involves gathering continuous streams of data from network devices, applications, and cloud infrastructure. Operators use both active and passive sensors to monitor live network traffic and application performance. Active sensors send test packets or simulate user activity, while passive sensors observe actual traffic without adding extra load.
Real-time data collection enables operators to detect issues such as latency spikes, packet loss, or bandwidth congestion before they impact users.
The efficiency of real-time data collection depends on monitoring key metrics. These metrics include latency, jitter, packet loss, bandwidth utilization, throughput, error rate, availability, round-trip time, and network efficiency. Each metric provides insight into the performance and reliability of the network and applications.
Metric | Description | Importance for Real-Time Data Collection Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
Latency | Time taken for a data packet to travel from source to destination, measured in milliseconds. | Low latency ensures timely data delivery, critical for real-time monitoring. |
Jitter | Variability in packet arrival times. | Consistent packet delivery is essential for real-time voice/video applications. |
Packet Loss | Percentage of data packets lost during transmission. | Low packet loss is vital to maintain data integrity and network reliability. |
Bandwidth Utilization | Percentage of network capacity currently in use. | Helps identify congestion and optimize resource allocation in real-time. |
Throughput | Actual data successfully transmitted over the network in a given time frame. | Indicates network's ability to handle traffic load efficiently. |
Error Rate | Frequency of corrupted packets during transmission. | High error rates signal hardware or interference issues affecting data quality. |
Availability | Percentage of time the network is operational and accessible. | High availability supports continuous real-time data collection and monitoring. |
Round-Trip Time (RTT) | Time for a signal to travel to the destination and back. | Critical for assessing network responsiveness in real-time scenarios. |
Network Efficiency | Measures how effectively network resources are used, including bandwidth and power efficiency. | Reflects overall operational effectiveness of real-time data collection systems. |
Network monitoring software uses telemetry systems to stream data from network elements. These systems often use brokers like Kafka to deliver up-to-the-second insights. Operators can monitor live network traffic, consolidate events, and correlate alarms from different sources. This approach supports rapid root cause analysis and reduces the time needed to resolve issues. Real-time dashboards and analytics help operators optimize network performance and detect anomalies quickly.
Alerting and Notifications
Network monitoring software uses alerting and notification systems to keep operators informed about network health. These systems monitor live network traffic and application metrics, comparing them against predefined thresholds. When the software detects abnormal behavior, it sends instant alerts to the operations team.
Operators can configure alerts for a wide range of network and application events. These include device failures, bandwidth spikes, high latency, packet loss, and security threats. The software supports multiple notification channels, such as email, SMS, push notifications, and integration with incident management platforms.
Timely alerts allow teams to respond to issues before they escalate, reducing downtime and improving service quality.
Network monitoring tools use several methods to detect and report issues:
Ping tests measure round-trip time to assess connectivity and latency.
Synthetic monitoring agents exchange traffic every 500 ms to test performance.
Threshold checks compare real-time metrics against baselines to spot deviations.
Speed tests and Iperf/Jperf assess bandwidth and throughput.
SNMP monitoring collects device status and bandwidth utilization.
These methods provide quantitative data that enable proactive detection and resolution of network problems. Operators can monitor network device health, application performance, and cloud infrastructure from a single dashboard. This unified approach ensures that no critical event goes unnoticed.
Automated Responses
Automated responses form a key part of modern network monitoring software. When the software detects a problem, it can trigger predefined actions without human intervention. These actions may include rerouting traffic, restarting applications, isolating faulty devices, or blocking suspicious activity.
Automated responses help telecom operators reduce manual workload, speed up incident resolution, and maintain high service availability.
Empirical studies show that automated models can outperform traditional approaches in detecting and preventing telecom network issues. For example, advanced event extraction models can analyze real network data, identify fraud patterns, and support targeted preventive strategies. These models improve detection accuracy and help operators respond to threats more effectively.
Network monitoring systems use automation to enforce policies, remediate faults, and optimize resource allocation. This capability is especially important in cloud environments, where network conditions can change rapidly. Automated responses ensure that network monitoring software can adapt to new threats and maintain reliable service for all applications.
By combining real-time data collection, instant alerts, and automated responses, network monitoring software provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring network devices, applications, and cloud infrastructure.
Types of Issues Detected
Performance Degradation
Telecom equipment monitoring software identifies performance degradation by continuously collecting and analyzing real-time data from network devices. Operators track key metrics such as latency, throughput, packet loss, and availability. These indicators help reveal slowdowns or interruptions in network services. For example, increased latency often signals delays in data delivery, which can affect application performance and user experience. Monitoring tools compare live data against predefined thresholds. When metrics like throughput drop or packet loss rises, the system generates alerts for immediate action.
Performance Metric | Measurement Unit | Role in Detecting Performance Degradation |
|---|---|---|
Throughput | Mbps | Measures data transmission speed; drops indicate potential degradation |
Latency | ms | Time for data travel; increases signal delays and performance issues |
Packet Loss | % | Percentage of lost packets; higher loss signals network problems |
Availability | % | Network uptime; lower availability reflects outages or instability |
Operators use these benchmarks to detect issues early and maintain high-quality network services.
Device Failures
Monitoring software plays a vital role in detecting device failures across the network. It uses protocols like SNMP and ICMP to gather real-time status updates from routers, switches, and servers. The software checks device health, uptime, and resource usage. When a device becomes unresponsive or shows abnormal behavior, the system sends instant alerts to administrators. Automated responses can restart failed devices or reroute traffic to minimize disruption. Continuous monitoring ensures that device failures do not go unnoticed, reducing downtime and supporting reliable network operations.
Monitoring tools perform ping tests to check device connectivity.
SNMP polling collects data on device status and resource utilization.
Alerts notify teams when devices fail or exceed performance thresholds.
Security Threats
Network monitoring software detects security threats by analyzing traffic patterns, user behavior, and system logs. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms aggregate data from multiple sources to identify suspicious activities. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) use machine learning to spot unusual actions that may indicate insider threats. Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) monitor for unauthorized access and block malicious traffic. Cloud security monitoring extends protection to virtual environments, detecting misconfigurations and unusual access attempts.
Network security monitoring collects and analyzes diverse data types, enabling security teams to detect intrusions, understand attacker tactics, and respond quickly to threats.
This comprehensive approach allows operators to address both known and emerging security risks, ensuring the safety of network infrastructure and application performance.
Benefits of Network Monitoring
Improved Reliability
Network monitoring increases reliability by providing continuous visibility into the health of network devices and services. Operators can detect and resolve issues before they cause outages. For example, ESTEL’s telecom rectifiers deliver uninterrupted energy, reducing system failures and downtime. Modular designs and AI integration help networks adapt to changing demands. New systems achieve up to 20% energy savings, supporting both operational efficiency and reliability. The following chart highlights key improvements:
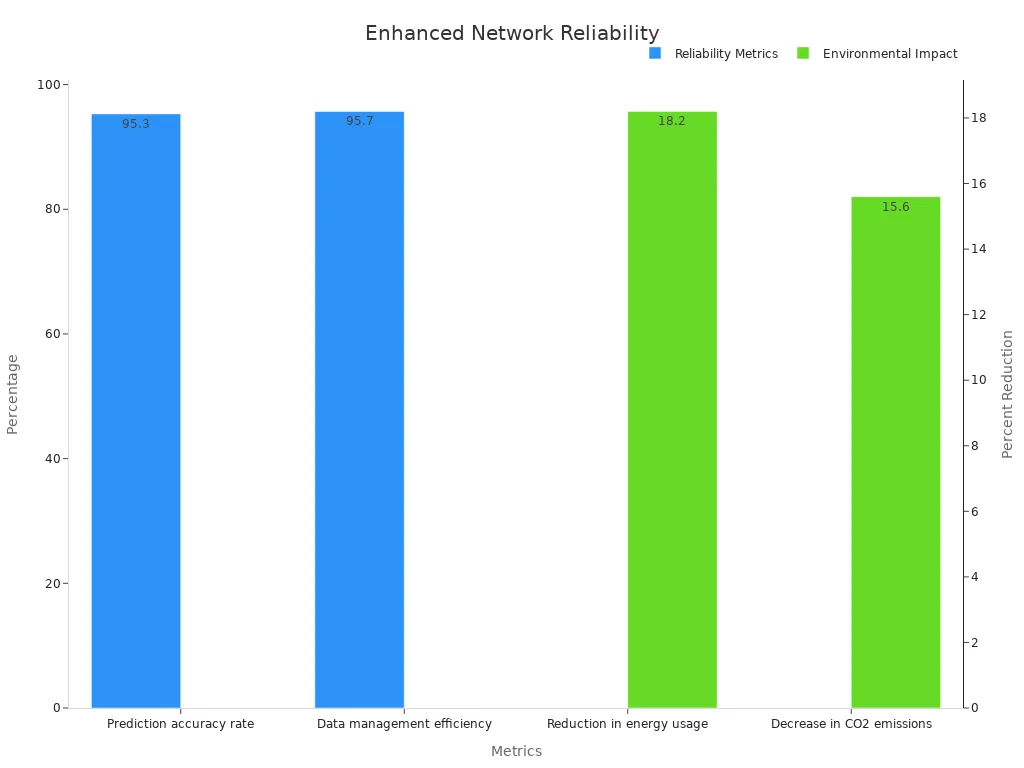
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Prediction accuracy rate | 95.3% |
Data management efficiency | 95.7% |
Reduction in energy usage | 18.2% |
Decrease in CO2 emissions | 15.6% |
Operational Efficiency
Network monitoring tools streamline operations by automating routine tasks and providing real-time insights. AI-driven software reduces manual workload and speeds up issue resolution. AT&T’s use of advanced monitoring tools improved decision-making by 59% and cut operational costs by 40%. Automation and predictive analytics help teams manage complex, multi-vendor environments, ensuring that network monitoring systems scale with business growth. Operators can focus on strategic projects while the software handles monitoring and troubleshooting.
Cost Savings
The benefits of network monitoring include significant cost savings. Predictable performance metrics allow for better forecasting and budgeting. Smarter infrastructure investments, guided by real-time data, optimize resource allocation. For instance, AT&T saw a 25% improvement in network reliability and a 40% reduction in operational costs after implementing advanced network monitoring software. Automation and analytics further reduce downtime, which lowers maintenance expenses and improves overall business performance.
SLA Compliance
Network monitoring ensures compliance with Service Level Agreements (SLAs) by tracking key performance metrics such as uptime, latency, and packet loss. Real-time dashboards and alerts enable operators to respond quickly to incidents, minimizing downtime and maintaining service quality. The table below shows how monitoring supports SLA compliance:
Performance Metric | Role in SLA Compliance |
|---|---|
Uptime/Availability | Detects outages promptly for high availability |
Incident Response Time | Enables quick acknowledgment and action |
Resolution Time | Facilitates faster issue resolution |
Latency | Maintains performance within SLA thresholds |
Packet Loss | Prevents SLA violations through early alerts |
Continuous SLA monitoring fosters trust with customers and supports business relationships. Proactive management and predictive analytics ensure that telecom operators meet service commitments and support innovation.
ESTEL telecom equipment monitoring software strengthens network reliability by using advanced monitoring, predictive analytics, and real-time alerts. Operators benefit from proactive detection and prevention of issues, which leads to higher uptime and lower maintenance costs. The following table highlights key features and their impact:
Feature | Impact |
|---|---|
Prevents overheating and hardware failure | |
Real-time Alerts & Insights | Reduces downtime with quick responses |
Predictive Maintenance | Forecasts failures for timely interventions |
Anomaly Detection Algorithms | Stops service disruptions before they spread |
IoT Integration | Automates responses and improves proactive maintenance |
Machine learning models analyze failure data for better prediction.
IoT sensors track critical network parameters in real time.
Automated alerts support fast maintenance actions.
Telecom operators can achieve greater efficiency and reliability by adopting ESTEL’s monitoring solutions. Requesting a demo allows teams to see how these tools transform network management.
FAQ
What types of telecom equipment does ESTEL monitoring software support?
ESTEL monitoring software supports a wide range of devices. These include routers, switches, servers, firewalls, and telecom rectifiers. The software also integrates with cloud-based and legacy systems.
How does the software alert operators about network issues?
The software sends instant alerts through email, SMS, push notifications, or integration with incident management platforms. Operators receive notifications as soon as the system detects abnormal network behavior.
Can ESTEL monitoring software help prevent security breaches?
Yes. The software analyzes traffic patterns and user activity. It uses intrusion detection and anomaly detection to identify threats. Operators can respond quickly to suspicious events and prevent security breaches.
Does the software require special training for operators?
Most operators learn to use the software quickly. The user interface is intuitive. ESTEL provides training resources and support to help teams get started and maximize the software’s benefits.
See Also
Understanding The Power System In ESTEL Telecom Cabinets
Best Practices For Monitoring Outdoor Telecom Cabinets Effectively
A Complete Guide To Risk Assessment Of Telecom Cabinet Batteries
Exploring ESTEL PDUs And Their Function Within Data Center Cabinets
Safety Features Of Custom ESTEL Outdoor Telecom Cabinet Designs
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA
