Top-Rated UPS Solutions for Telecom Industry

Reliable power forms the backbone of telecom operations. Even brief power cuts can disrupt wireless service, leading to significant financial losses—averaging $4.8 million per hour. Severe weather and human error contribute to frequent outages, making robust UPS for Telecom systems essential.
Metric Description | Numerical Data |
|---|---|
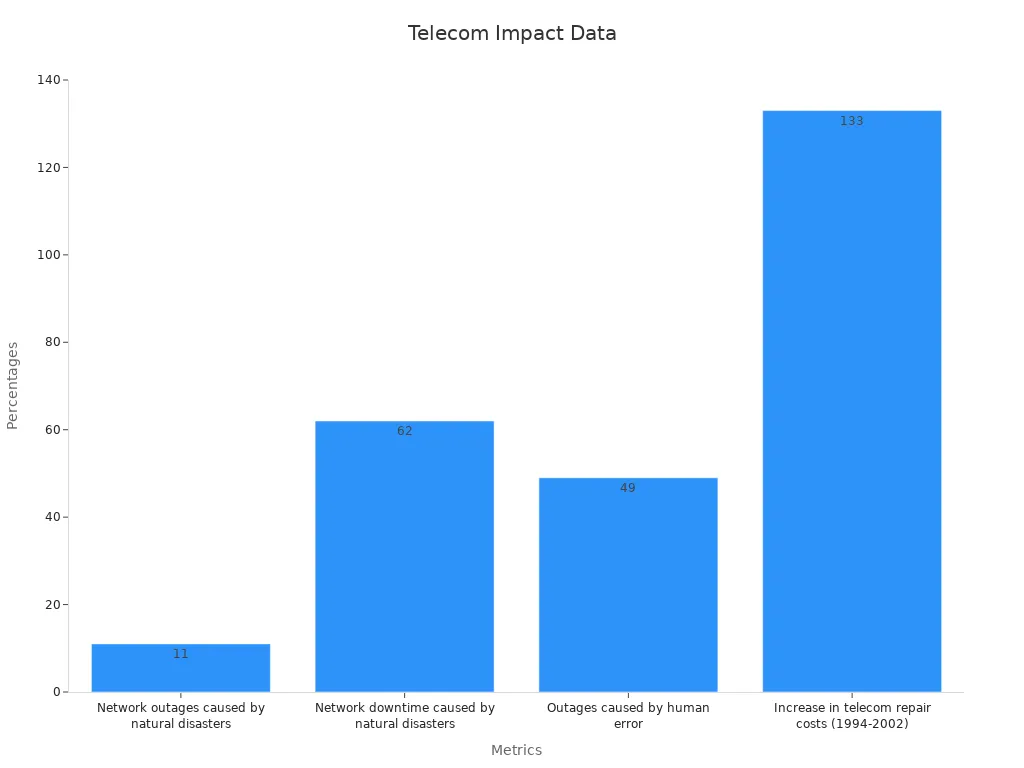
Network outages caused by natural disasters | 11% |
Network downtime caused by natural disasters | 62% |
Outages caused by human error | 49% |
Average cost of wireless service disruption | $4.8 million per hour |
Telecom providers must address power cuts to maintain high network reliability and protect critical infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
Reliable UPS systems are essential for telecom networks to prevent costly outages and protect sensitive equipment during power cuts.
Double conversion online UPS technology offers continuous, clean power with zero transfer time, making it ideal for telecom applications.
Advanced UPS features like lithium-ion batteries, real-time monitoring, and surge protection improve reliability and reduce downtime.
Choosing the right UPS involves assessing power needs, runtime, scalability, and surge protection to match specific telecom environments.
Regular maintenance and remote monitoring keep UPS systems efficient, extend battery life, and ensure uninterrupted telecom service.
UPS for Telecom

Importance
Telecom companies depend on continuous power to keep networks running and prevent service interruptions. UPS for telecom systems play a vital role in bridging the gap during power cuts, ensuring that data transmission and emergency communications remain uninterrupted. Without reliable battery backup, telecom operators risk costly downtime and potential equipment damage. Severe weather causes over half of power outages in the United States, making robust battery backup solutions essential for both urban and remote telecom sites.
ESTEL systems deliver uninterrupted power supply during outages, which is critical for telecom data transmission and emergency communications.
Advanced lithium-ion batteries in these systems provide extended runtime, high energy efficiency, and reliability in extreme temperatures.
Hybrid power solutions, which combine UPS for telecom, generators, and renewable energy sources, ensure power continuity in off-grid and unreliable grid locations.
Real-time monitoring and battery management optimize performance and reduce downtime.
Modular and scalable designs adapt to diverse telecom network demands, from dense urban 5G to rural installations.
Double conversion online UPS for telecom stands out as the preferred technology, especially for mobile towers. This approach delivers seamless power transfer and superior surge protection, shielding sensitive equipment from voltage fluctuations and outages. As telecom networks expand, the demand for reliable battery backup and advanced surge protection continues to grow.
Key Features
Effective UPS for telecom systems must offer more than just basic battery backup. High-performance batteries operate reliably in extreme heat, cold, and humidity, ensuring uninterrupted service. Power Distribution Units (PDUs) with surge protection, circuit breakers, and monitoring capabilities provide stable and safe power delivery. Efficient rectifiers convert AC to DC power and regulate voltage, protecting sensitive telecom equipment.
Smart monitoring systems enable real-time oversight, remote access, and alarms to address issues proactively. Teleprotection systems isolate faults by disconnecting faulty network parts, preventing damage and reducing outage time. Advanced features such as predictive maintenance, load balancing, and thermal management enhance reliability and extend equipment lifespan. Seamless integration with existing telecom infrastructure and rugged design ensure consistent performance, even in harsh environments. Surge protection remains a top priority, as it minimizes downtime and safeguards critical assets.
Top Solutions
Overview
The telecom industry relies on advanced UPS solutions to maintain uninterrupted service and protect critical infrastructure. Leading manufacturers have developed specialized systems that address the unique demands of telecom networks. The most recognized brands in this sector include Eaton, Vertiv, Schneider Electric (APC), Toshiba, ABB, Mitsubishi Electric, Delta Electronics, General Electric, and CyberPower. These companies have established a strong presence by delivering reliable, scalable, and efficient UPS for telecom applications.
Note: Market analysis shows that double conversion online UPS systems dominate the global UPS market. Their high energy efficiency and ability to filter frequency variations help preserve battery life. Telecom operators prefer this topology because it provides continuous power backup, meeting the increasing demand for reliability in critical sectors.
The Mitsubishi Electric 9900AEGIS UPS, which uses true online double conversion technology, demonstrates exceptional reliability. It maintains a sustained load carrying capability of 99.9995% based on operational history. Features such as minimal voltage distortion, dynamic inverter response, and low maintenance design ensure dependable power delivery in demanding telecom environments.
The following table highlights key statistics that validate the market share and performance of top UPS solution providers within the broader telecom ecosystem:
Statistic Category | Details |
|---|---|
Total Telco NI Vendor Revenue | $49.6B in 3Q24; $205.7B annualized 3Q24 |
Year-over-Year Revenue Change | +0.3% in 3Q24 quarter; -5.6% annualized 3Q24 |
Market Share of Top 3 Vendors | Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia combined hold 37.5% annualized 3Q24; 33.6% in 3Q24 quarter |
Number of Vendors Tracked | 134 Telco NI vendors (108 actively selling to telcos) |
Top Vendors by YoY Growth | Tejas Networks and Broadcom (due to BSNL 4G rollout and VMWare acquisition respectively) |
Capex Spending Outlook | Expected decline from $314B in 2023 to just below $300B in 2024; projected ~$280B by 2028 |
Market Influence | Huawei significantly lifted market performance, offsetting declines elsewhere |
These figures reflect the robust demand for reliable power solutions, including UPS for telecom, across the global telecommunications landscape.
Comparison
Each leading UPS manufacturer brings unique strengths to telecom applications. The following table summarizes the main advantages and limitations of top brands:
Manufacturer | Strengths | Weaknesses | Relevant Telecom/Data Center Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Eaton | Reliable power backup; energy efficient; advanced real-time monitoring; flexible installation; scalable; hot-swappable UPS functionality; sustainable design | Higher initial cost | Prioritizes reliability, energy efficiency, and sustainability; suitable for growing data centers requiring continuous power |
Vertiv | Modular and scalable PDUs; intelligent with remote monitoring; strong thermal management; robust build quality; supports dual voltage (120V/208V); secure receptacles to prevent disconnections | Higher upfront cost | Ideal for scalable operations needing flexible voltage support and robust, intelligent power distribution |
Schneider Electric | Wide range of UPS models; high market presence; reliable backup power and surge protection | Potentially high cost; varied quality | Leading manufacturer with diverse offerings, but cost and quality may vary across models |
Toshiba | High reliability; advanced battery management; compact designs | Limited global service network | Well-suited for remote telecom sites and compact installations |
ABB | Industrial-grade durability; strong surge protection; energy-efficient designs | Complex integration | Preferred for harsh environments and mission-critical telecom infrastructure |
Mitsubishi Electric | Exceptional reliability; low maintenance; advanced double conversion technology | Premium pricing | Proven performance in demanding telecom and data center environments |
Delta Electronics | High efficiency; flexible configurations; competitive pricing | Limited high-capacity models | Good fit for small to mid-sized telecom installations |
General Electric | Robust engineering; global support; advanced diagnostics | Higher maintenance requirements | Trusted for large-scale telecom and utility applications |
CyberPower | Cost-effective solutions; user-friendly interfaces; compact form factors | Limited advanced features | Suitable for small telecom sites and edge deployments |
Tip: Double conversion online UPS models remain the most suitable choice for telecom environments. They deliver seamless power transfer, superior surge protection, and continuous backup, which are essential for maintaining network uptime.
Manufacturers such as Eaton, Vertiv, and Schneider Electric lead the market by offering solutions that combine reliability, scalability, and advanced monitoring. Eaton focuses on energy efficiency and sustainability, making it ideal for expanding networks. Vertiv excels in modularity and intelligent power distribution, supporting flexible deployment. Schneider Electric provides a broad product range, ensuring options for diverse telecom needs, though cost and quality may vary.
Other brands like Toshiba and ABB offer specialized features for remote or harsh environments, while Mitsubishi Electric stands out for its operational reliability and low maintenance. Delta Electronics and CyberPower provide cost-effective options for smaller installations.
Telecom operators should evaluate each brand's strengths in relation to their specific network requirements. The right UPS for telecom will ensure continuous service, protect sensitive equipment, and support future network growth.
Uninterruptible Power Supply Selection
Criteria
Selecting the right uninterruptible power supply for telecom operations requires careful evaluation of several technical factors. Telecom providers must ensure that the system delivers reliable battery backup and robust surge protection. The following criteria help determine the best fit for demanding telecom environments:
Runtime: The UPS must provide sufficient battery backup to bridge power interruptions and allow for safe shutdown or generator startup.
Voltage regulation: Stable voltage output protects sensitive telecom equipment from fluctuations and ensures consistent performance.
Network management: Advanced monitoring and remote management capabilities enable real-time oversight and rapid response to issues.
Scalability: Modular designs allow for easy expansion as network demands grow.
Surge protection: Effective systems shield equipment from voltage spikes and electrical disturbances.
Engineers also evaluate UPS performance using specific tests to ensure reliability in telecom settings:
Conducted emissions on input and output lines
Radiated emissions
Current harmonic tests
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) tests
Electrical fast transient tests
Radiated immunity tests
Low frequency immunity tests
These tests confirm that the uninterruptible power supply can operate reliably in environments with high electromagnetic interference, which is common in telecom facilities.
Battery health monitoring plays a critical role in maintaining continuous battery backup and surge protection. Operators track voltage and temperature of individual battery cells, use remote monitoring systems, and analyze battery trends to prevent failures. Monitoring systems must support various battery types and large cell counts, ensuring early detection of weak cells and abnormal temperature rises.
Application Scenarios
Telecom networks present diverse application scenarios, each with unique power protection needs. Mobile towers require compact, rugged UPS systems that deliver instant battery backup and advanced surge protection during outages. Data centers, especially large facilities, depend on double conversion UPS solutions to maintain continuous operations and protect mission-critical hardware. Smaller data centers often use standby or line interactive UPS models for cost-effective surge protection and battery backup.
Remote sites and installations in harsh environments demand UPS systems with high energy efficiency, modularity, and lithium-ion batteries. These features ensure reliable battery backup and surge protection even in extreme temperatures or unstable grid conditions. Real-time remote monitoring and energy storage integration further enhance system reliability, allowing operators to address issues before they impact network performance.
Specialized UPS solutions for telecom infrastructure, such as those used in mobile base stations and broadband hubs, provide seamless power switchover and scalable surge protection. These systems support uninterrupted service, safeguard equipment, and adapt to the evolving needs of modern telecom networks.
Comparison
Technical Specs
Telecom operators evaluate UPS solutions based on battery technology, system topology, and surge protection features.
Nickel-cadmium batteries last up to 20 years and perform well in high temperatures, but they cost more and require careful disposal.
Lithium-ion batteries offer twice the lifespan of lead-acid batteries, reach about 95% efficiency, recharge quickly, and include integrated monitoring.
Lead-acid batteries provide lower efficiency (about 70%), shorter lifespans, and need more cooling, which increases operational costs.
Modern lithium-ion batteries now address earlier safety concerns, making them a preferred choice for telecom UPS systems.
UPS topologies also matter:
Online UPS systems deliver continuous, high-quality AC power with zero transfer time and perfect sine wave output, ensuring maximum surge protection.
Line-interactive UPS systems provide power conditioning and battery backup with a 4-6 millisecond transfer time, suitable for moderate surge protection needs.
Offline UPS systems switch to battery in 6-8 milliseconds, offering basic surge protection for less critical applications.
Reliability
Reliability remains a top priority for telecom networks.
Online UPS systems maintain uptime with frequency error below 0.5%, frequency fluctuation rate under 0.25%, and total harmonic distortion less than 1%.
Inverter efficiency reaches at least 95%, supporting stable power delivery and robust surge protection.
Key reliability metrics include uptime, availability, fault tolerance, resilience, mean time between failures (MTBF), and mean time to repair (MTTR).
Battery runtime, efficiency, and load handling capacity also influence reliability. Online UPS models support the highest loads and longest runtimes, making them ideal for telecom environments that demand continuous surge protection.
Metric | Description | UPS Types and Notes |
|---|---|---|
Battery Runtime | Duration UPS can supply power during outage before battery depletion | Offline: Short; Line-Interactive: 10-30 min; Online: Longer, varies by battery; Delta-Conversion: Longest |
Efficiency | Energy conversion efficiency impacting operating cost and heat generation | Offline: Highest under normal; Line-Interactive: Moderate; Online: Lower due to double conversion; Delta: Highest |
Load Handling | Maximum power UPS can supply to connected devices | Offline: Up to ~1,000 VA; Line-Interactive: 1,000-3,000 VA; Online: Up to 1,000 kVA+; Delta: High-load environments |
Reliability & Longevity | Lifespan of batteries, maintenance frequency, component quality affecting uptime and durability | Offline: Reliable for small loads; Line-Interactive: Better; Online: Excellent with maintenance; Delta: Highly reliable |
Cost
Cost-effectiveness shapes UPS selection in telecom.
Major manufacturers focus on energy efficiency and surge protection to reduce operational expenses. Lithium-ion batteries, while more expensive upfront, lower total cost of ownership through longer lifespan and reduced maintenance.
A comprehensive cost analysis considers system capacity, redundancy, battery type, energy efficiency, and service costs. Operators should evaluate both initial investment and ongoing expenses, including maintenance and energy consumption.
Market trends show growing demand for reliable power and surge protection in telecom, driving innovation in cost-effective UPS solutions.
A thorough total cost of ownership analysis helps telecom providers identify the most suitable uninterruptible power supply for their needs.
Selection Tips
Power Needs
Telecom operators must start by accurately assessing power requirements. A detailed audit of electricity usage helps determine the total wattage of all critical telecom and business equipment. Using watt-meters or reviewing device nameplate data provides precise measurements. Operators should include a safety margin—typically around 25%—to account for future growth and unexpected power fluctuations. Identifying which systems require uninterrupted battery backup, such as telecommunications gear and servers, ensures that essential operations remain protected. Operators must also evaluate how long their networks can tolerate downtime, which guides the selection of appropriate battery backup duration. Understanding the differences between UPS types—standby, line-interactive, and double-conversion—helps match efficiency and protection levels to specific telecom needs. Sizing the UPS in volt-amps (VA) to match the cumulative load prevents overloading and unnecessary spending. Planning for battery life, maintenance, and replacement supports long-term reliability.
Operators should use real-world power consumption data to select a UPS that delivers consistent battery backup and power quality tailored to telecom infrastructure.
Deployment
Deploying UPS systems in telecom environments requires careful planning. Lithium-ion batteries offer longer life expectancy and lower operational risk compared to traditional VRLA batteries, making them a preferred choice for battery backup. Operators should balance capital costs with system availability, using redundancy strategies like N+1 or 2N configurations to enhance reliability. UPS systems must support not only IT equipment but also cooling systems, especially in high-density environments, to prevent thermal overload. Battery backup runtimes should align with the network’s risk tolerance, ranging from seconds to several minutes. Modern UPS designs achieve energy efficiencies up to 98%, reducing cooling and energy costs. Modular and scalable architectures allow telecom operators to expand power capacity as needed, avoiding over-provisioning. Strategic placement of UPS units ensures easy maintenance access and optimal cooling. Advanced monitoring tools help track battery health and system performance in real time.
Maintenance
A proactive maintenance plan ensures continuous battery backup and system reliability. Regular UPS maintenance prevents costly downtime and data loss. Redundant configurations, such as N+1 and parallel systems, provide load sharing and simplify maintenance. Operators should schedule maintenance checks at least twice a year to identify issues early and minimize failure risks. Proper battery management and timely replacement extend UPS lifespan and maintain efficiency. Compliance with industry regulations, including BS62485 and BS 7671:2018, supports safety and long-term performance. Proactive maintenance enables early fault detection, reducing financial and operational risks for telecom networks.
Regular maintenance and monitoring protect uptime and data integrity, which are critical for telecom operations.
Telecom operators benefit most from double conversion online UPS systems by Eaton, Vertiv, and Schneider Electric. These solutions deliver unmatched reliability and advanced monitoring. Matching UPS features to network requirements ensures optimal performance. Operators should regularly review their power infrastructure and plan for future growth.
For expert guidance, telecom professionals can consult with UPS specialists or request a tailored assessment to secure uninterrupted service.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of double conversion online UPS for telecom?
Double conversion online UPS systems provide continuous, clean power. They protect sensitive telecom equipment from voltage fluctuations and outages. This technology ensures zero transfer time, which keeps networks running without interruption.
How often should telecom operators perform UPS maintenance?
Operators should schedule UPS maintenance at least twice a year. Regular checks help identify battery issues early and prevent unexpected downtime. Proactive maintenance extends system lifespan and maintains network reliability.
Which battery type offers the best performance for telecom UPS systems?
Battery Type | Lifespan | Efficiency | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
Lithium-ion | Long | High | Low |
Lead-acid | Medium | Moderate | Moderate |
Nickel-cadmium | Long | High | Moderate |
Lithium-ion batteries deliver the best performance for most telecom applications.
Can UPS systems support remote monitoring and management?
Yes, modern UPS solutions include remote monitoring features.
Operators can track battery health, receive alerts, and manage power systems from any location.
Remote management improves response times and reduces operational risks.
See Also
Steps To Guarantee Consistent Power For Telecom Cabinets
Key Insights Into Features Of Telecom Power Supplies
Reasons Lithium Batteries Excel Over Others In Telecom Cabinets
Solar Energy Storage Solutions For Telecom Cabinet Power Systems
Methods To Calculate Power And Battery Needs For Telecom Cabinets
CALL US DIRECTLY
86-13752765943
3A-8, SHUIWAN 1979 SQUARE (PHASE II), NO.111, TAIZI ROAD,SHUIWAN COMMUNITY, ZHAOSHANG STREET, NANSHAN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA
